CircSETD3 (Hsa_circ_0000567) acts as a sponge for microRNA-421 inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth
- PMID: 30795787
- PMCID: PMC6385474
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1041-2
CircSETD3 (Hsa_circ_0000567) acts as a sponge for microRNA-421 inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma growth
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play important roles in tumourigenesis and tumour progression. However, the expression profiles and functions of circRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are largely unclear.
Methods: The expression profiles of circRNAs in HCC were identified through microarray analysis and were validated through quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. The circular structure of candidate circRNA was confirmed through Sanger sequencing, divergent primer PCR, and RNase R treatments. Proliferation of HCC cells was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The microRNA (miRNA) sponge mechanism of circRNAs was demonstrated using dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation assays.
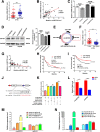
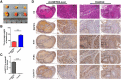
Results: CircSETD3 (hsa_circRNA_0000567/hsa_circRNA_101436) was significantly downregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Low expression of circSETD3 in HCC tissues significantly predicted an unfavourable prognosis and was correlated with larger tumour size and poor differentiation of HCC in patients. In vitro experiments showed that circSETD3 inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells and induced G1/S arrest in HCC cells. In vivo studies revealed that circSETD3 was stably overexpressed in a xenograft mouse model and inhibited the growth of HCC. Furthermore, we demonstrated that circSETD3 acts as a sponge for miR-421 and verified that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)14 is a novel target of miR-421.
Conclusion: CircSETD3 is a novel tumour suppressor of HCC and is a valuable prognostic biomarker. Moreover, circSETD3 inhibits the growth of HCC partly through the circSETD3/miR-421/MAPK14 pathway.
Keywords: Circular RNA; Growth; Hepatocellular carcinoma; SETD3; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The collection of human specimens was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of West China Hospital and the written informed consent were obtained from each patient.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0016788 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis through miR-486/CDK4 pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):500-508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26612. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29923236
-
Circular RNA circ-102,166 acts as a sponge of miR-182 and miR-184 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Apr;44(2):279-295. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00564-y. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 33034848
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_103809 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-620.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Feb;23(2):555-566. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201902_16868. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30720163
-
Progress and prospects of circular RNAs in Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel insights into their function.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4408-4422. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26154. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28833094 Review.
-
Circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Biomarkers, functions and mechanisms.Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;231:116660. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116660. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31319086 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA CircEPB41L2 Functions as Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Sponging miR-590-5p.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Apr 1;13:2969-2981. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S291682. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33833580 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circNHSL1 Contributes to Gastric Cancer Progression Through the miR-149-5p/YWHAZ Axis.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 12;12:7117-7130. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S253152. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32848466 Free PMC article.
-
The SRSF1/circATP5B/miR-185-5p/HOXB5 feedback loop regulates the proliferation of glioma stem cells via the IL6-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 15;40(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01931-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33858489 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of clinical application of lenvatinib and its resistance mechanism in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4113-4171. doi: 10.62347/UJVP4361. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(10):5438-5445. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15258. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32281724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, Gores G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell S, Park SH. The epidemiology of hepatocellular cancer: from the perspectives of public health problem to tumour biology. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(Suppl 19):96–101. - PubMed
-
- Marquardt JU, Andersen JB, Thorgeirsson SS. Functional and genetic deconstruction of the cellular origin in liver cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(11):653–667. - PubMed
-
- Franssen B, Alshebeeb K, Tabrizian P, Marti J, Pierobon ES, Lubezky N, et al. Differences in surgical outcomes between hepatitis B- and hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of a single north American center. Ann Surg. 2014;260(4):650–656. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 71673193/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2015SZ0131/Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Sichuan Province
- 2017FZ0082/Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Sichuan Province
- 19ZDYF1740/Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Sichuan Province
- 18JR3RA058/Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists and the Science & Technology Planning Project of Gansu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

