Combining naproxen and a dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist improves pain and structural outcomes in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model
- PMID: 30795801
- PMCID: PMC6387482
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1819-9
Combining naproxen and a dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist improves pain and structural outcomes in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model
Abstract
Background: Pain is a debilitating symptom of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), caused by joint inflammation and cartilage and bone destruction. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to treat pain and inflammation in RA, but are not disease-modifying and do not prevent joint destruction when administered alone. KBPs (Key Bioscience peptides) are synthetic peptides based on salmon calcitonin and are expected to inhibit bone resorption and to be chondroprotective. In this study, we investigated if combining a standard of care NSAID (naproxen) with a KBP resulted in improvement in pain scores, as well as disease activity and structural damage in a rat model of RA.
Methods: Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) was induced in 40 female Lewis rats by immunization with porcine type II collagen; 10 rats were given sham injections. CIA rats were treated with KBP and/or naproxen. Health scores and joint scores were evaluated daily. Mechanical and cold allodynia tests and burrowing tests were used to assess pain-like behaviors. Blood samples were collected for biomarker testing, and paws were collected for histology and microcomputed tomography.
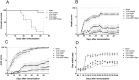
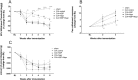
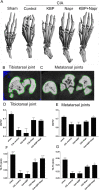
Results: Naproxen monotherapy increased the time until humane endpoints was reached, and improved health score, pain assessments, and trabecular thickness, while KBP monotherapy did not result in improvements. Combination therapy had improved efficacy over naproxen monotherapy; combination therapy resulted in improved health scores, and importantly reduced mechanical and cold allodynia assessment. Furthermore, protection of articular cartilage structure and preservation of bone structure and bone volume were also observed.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that combining KBP and naproxen may be a relevant therapeutic strategy for RA, resulting in improvements to the overall health, pain, inflammation, and joint structure.
Keywords: Bone; CIA; DACRA; NSAIDs; Pain; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Welfare Division of the Danish Ministry of Justice under the institutional license issued to Nordic Bioscience (2014-15-0201-00097).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
AK, MAK, KVA, CST, and KH are employees of Nordic Bioscience A/S which is a company involved in the discovery and development of biochemical biomarkers and novel therapeutic peptides, including KBPs. HL is a former employee of Nordic Bioscience A/S. KH, KVA, and MAK hold patents on KBPs. MAK and KH hold stocks in Nordic Bioscience A/S. AD and MD declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist inhibits pain behavior and reduces cartilage pathology in an osteoarthritis rat model.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Sep;27(9):1339-1346. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.05.016. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 31176015
-
Does receptor balance matter? - Comparing the efficacies of the dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists cagrilintide and KBP-336 on metabolic parameters in preclinical models.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Dec;156:113842. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113842. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36242844
-
The dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonist KBP-336 elicits a unique combination of weight loss, antinociception and bone protection - a novel disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jul 12;26(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03361-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38997785 Free PMC article.
-
Central control of energy balance by amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists and their potential for treatment of metabolic diseases.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020 Sep;127(3):163-177. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13427. Epub 2020 May 18. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32363722 Review.
-
Amylin and Calcitonin: Potential Therapeutic Strategies to Reduce Body Weight and Liver Fat.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 8;11:617400. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.617400. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33488526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcitonin treatment for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis - a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical data.EFORT Open Rev. 2024 Jul 1;9(7):600-614. doi: 10.1530/EOR-23-0133. EFORT Open Rev. 2024. PMID: 38949173 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-27a-3p promotes the osteogenic differentiation by activating CRY2/ERK1/2 axis.Mol Med. 2021 Apr 26;27(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00303-5. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33902432 Free PMC article.
-
The calcitonin receptor protects against bone loss and excessive inflammation in collagen antibody-induced arthritis.iScience. 2021 Dec 24;25(1):103689. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103689. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35036874 Free PMC article.
-
Biochanin A inhibits endothelial dysfunction induced by IL‑6‑stimulated endothelial microparticles in Perthes disease via the NFκB pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Feb 13;27(4):137. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12425. eCollection 2024 Apr. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38476892 Free PMC article.
-
Naproxen treatment inhibits articular cartilage loss in a rat model of osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2021 Oct;39(10):2252-2259. doi: 10.1002/jor.24937. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Orthop Res. 2021. PMID: 33274763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

