MiR-9 promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis and is activated by MYC and OCT4 in human glioma
- PMID: 30795814
- PMCID: PMC6385476
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1078-2
MiR-9 promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis and is activated by MYC and OCT4 in human glioma
Abstract
Background: Glioma, characterized by its undesirable prognosis and poor survival rate, is a serious threat to human health and lives. MicroRNA-9 (miR-9) is implicated in the regulation of multiple tumors, while the mechanisms underlying its aberrant expression and functional alterations in human glioma are still controversial.
Methods: Expressions of miR-9 were measured in GEO database, patient specimens and glioma cell lines. Gain- and loss-of-function assays were applied to identify the effects of miR-9 on glioma cells and HUVECs in vitro and in vivo. Potential targets of miR-9 were predicted by bioinformatics and further verified via in vitro experiments. Transcriptional regulation of miR-9 by MYC and OCT4 was determined in glioma cells.
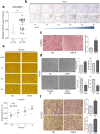
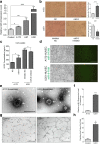
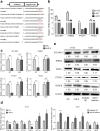
Results: MiR-9 was frequently up-regulated in glioma specimens and cells, and could significantly enhance proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells. In addition, miR-9 could be secreted from glioma cells via exosomes and was then absorbed by vascular endothelial cells, leading to an increase in angiogenesis. COL18A1, THBS2, PTCH1 and PHD3 were verified as the direct targets of miR-9, which could elucidate the miR-9-induced malignant phenotypes in glioma cells. MYC and OCT4 were able to bind to the promoter region of miR-9 to trigger its transcription.
Conclusions: Our results highlight that miR-9 is pivotal for glioma pathogenesis and can be treated as a potential therapeutic target for glioma.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Glioma; MYC; OCT4; Tumorigenesis; miR-9.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Xijing Hospital affiliated to FMMU. This work was performed according to the ethical standards of Declaration of Helsinki and written informed consent was obtained from all the patients ahead of the experiments. Animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of FMMU, and was strictly implemented according to institutional guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Miller CR, Glioblastoma PA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131(3):397–406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

