Membrane-Binding Cooperativity and Coinsertion by C2AB Tandem Domains of Synaptotagmins 1 and 7
- PMID: 30795874
- PMCID: PMC6428868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.01.035
Membrane-Binding Cooperativity and Coinsertion by C2AB Tandem Domains of Synaptotagmins 1 and 7
Abstract
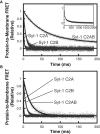
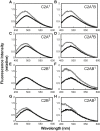
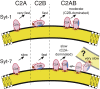
Synaptotagmin-1 (Syt-1) and synaptotagmin-7 (Syt-7) contain analogous tandem C2 domains, C2A and C2B, which together sense Ca2+ to bind membranes and promote the stabilization of exocytotic fusion pores. Syt-1 triggers fast release of neurotransmitters, whereas Syt-7 functions in processes that involve lower Ca2+ concentrations such as hormone secretion. Syt-1 C2 domains are reported to bind membranes cooperatively, based on the observation that they penetrate farther into membranes as the C2AB tandem than as individual C2 domains. In contrast, we previously suggested that the two C2 domains of Syt-7 bind membranes independently, based in part on measurements of their liposome dissociation kinetics. Here, we investigated C2A-C2B interdomain cooperativity with Syt-1 and Syt-7 using directly comparable measurements. Equilibrium Ca2+ titrations demonstrate that the Syt-7 C2AB tandem binds liposomes lacking phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) with greater Ca2+ sensitivity than either of its individual domains and binds to membranes containing PIP2 even in the absence of Ca2+. Stopped-flow kinetic measurements show differences in cooperativity between Syt-1 and Syt-7: Syt-1 C2AB dissociates from PIP2-free liposomes much more slowly than either of its individual C2 domains, indicating cooperativity, whereas the major population of Syt-7 C2AB has a dissociation rate comparable to its C2A domain, suggesting a lack of cooperativity. A minor subpopulation of Syt-7 C2AB dissociates at a slower rate, which could be due to a small cooperative component and/or liposome clustering. Measurements using an environment-sensitive fluorescent probe indicate that the Syt-7 C2B domain inserts deeply into membranes as part of the C2AB tandem, similar to the coinsertion previously reported for Syt-1. Overall, coinsertion of C2A and C2B domains is coupled to cooperative energetic effects in Syt-1 to a much greater extent than in Syt-7. The difference can be understood in terms of the relative contributions of C2A and C2B domains toward membrane binding in the two proteins.
Copyright © 2019 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lateral diffusion of proteins on supported lipid bilayers: additive friction of synaptotagmin 7 C2A-C2B tandem domains.Biochemistry. 2014 Dec 23;53(50):7904-13. doi: 10.1021/bi5012223. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25437758 Free PMC article.
-
Exceptionally tight membrane-binding may explain the key role of the synaptotagmin-7 C2A domain in asynchronous neurotransmitter release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):E8518-E8527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710708114. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28923929 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin C2B domain regulates Ca2+-triggered fusion in vitro: critical residues revealed by scanning alanine mutagenesis.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 14;283(46):31763-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803355200. Epub 2008 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18784080 Free PMC article.
-
The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Mar;29(3):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15003272 Review.
-
The functional significance of synaptotagmin diversity in neuroendocrine secretion.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Sep 18;4:124. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00124. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 24065953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptotagmin-7 outperforms synaptotagmin-1 to promote the formation of large, stable fusion pores via robust membrane penetration.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 27;14(1):7761. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42497-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38012142 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning to decompose macromolecules into independent Markovian domains.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 19;13(1):7101. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34603-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36402768 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-7 places dense-core vesicles at the cell membrane to promote Munc13-2- and Ca2+-dependent priming.Elife. 2021 Mar 22;10:e64527. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64527. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33749593 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalent lipid targeting by the calcium-independent C2A domain of synaptotagmin-like protein 4/granuphilin.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100159. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014618. Epub 2020 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33277360 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane Membrane Readers form a Novel Class of Proteins That Include Peripheral Phosphoinositide Recognition Domains and Viral Spikes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;12(11):1161. doi: 10.3390/membranes12111161. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brose N., Petrenko A.G., Jahn R. Synaptotagmin: a calcium sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science. 1992;256:1021–1025. - PubMed
-
- Chapman E.R. How does synaptotagmin trigger neurotransmitter release? Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008;77:615–641. - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson N., Han W. Calcium-sensing beyond neurotransmitters: functions of synaptotagmins in neuroendocrine and endocrine secretion. Biosci. Rep. 2009;29:245–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

