Cohesin occupancy and composition at enhancers and promoters are linked to DNA replication origin proximity in Drosophila
- PMID: 30796039
- PMCID: PMC6442380
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.243832.118
Cohesin occupancy and composition at enhancers and promoters are linked to DNA replication origin proximity in Drosophila
Abstract
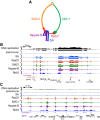
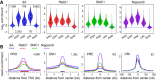
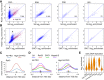
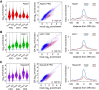
Cohesin consists of the SMC1-SMC3-Rad21 tripartite ring and the SA protein that interacts with Rad21. The Nipped-B protein loads cohesin topologically around chromosomes to mediate sister chromatid cohesion and facilitate long-range control of gene transcription. It is largely unknown how Nipped-B and cohesin associate specifically with gene promoters and transcriptional enhancers, or how sister chromatid cohesion is established. Here, we use genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation in Drosophila cells to show that SA and the Fs(1)h (BRD4) BET domain protein help recruit Nipped-B and cohesin to enhancers and DNA replication origins, whereas the MED30 subunit of the Mediator complex directs Nipped-B and Vtd in Drosophila (also known as Rad21) to promoters. All enhancers and their neighboring promoters are close to DNA replication origins and bind SA with proportional levels of cohesin subunits. Most promoters are far from origins and lack SA but bind Nipped-B and Rad21 with subproportional amounts of SMC1, indicating that they bind cohesin rings only part of the time. Genetic data show that Nipped-B and Rad21 function together with Fs(1)h to facilitate Drosophila development. These findings show that Nipped-B and cohesin are differentially targeted to enhancers and promoters, and suggest models for how SA and DNA replication help establish sister chromatid cohesion and facilitate enhancer-promoter communication. They indicate that SA is not an obligatory cohesin subunit but a factor that controls cohesin location on chromosomes.
© 2019 Pherson et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Brough R, Bajrami I, Vatcheva R, Natrajan R, Reis-Filho JS, Lord CJ, Ashworth A. 2012. APRIN is a cell cycle specific BRCA2-interacting protein required for genome integrity and a predictor of outcome after chemotherapy in breast cancer. EMBO J 31: 1160–1176. 10.1038/emboj.2011.490 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
