CIK cell-based delivery of recombinant adenovirus KGHV500 carrying the anti-p21Ras scFv gene enhances the anti-tumor effect and safety in lung cancer
- PMID: 30796510
- PMCID: PMC11810408
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-019-02857-8
CIK cell-based delivery of recombinant adenovirus KGHV500 carrying the anti-p21Ras scFv gene enhances the anti-tumor effect and safety in lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Adenovirus (Ads) is one of the most popular vectors used in gene therapy for the treatment of cancer. However, systemic therapy is limited by circulating antiviral antibodies and poor viral delivery in vivo. In this study, we used cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells as delivery vehicles of Ads KGHV500 carrying the anti-p21Ras scFv gene to treat Ras gene-related lung cancer and investigate the anti-tumor effect in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: The human lung cancer cell line A549 was employed to investigate the anti-tumor activity of recombinant Ads KGHV500 harboring the anti-p21Ras scFv gene using MTT, wound healing, transwell invasion, and apoptosis assays in vitro. Next, CIK cells were used as delivery vehicles to deliver KGHV500 carrying the anti-p21Ras scFv gene to treat A549-transplanted tumors in nude mice, and viral replication, p21Ras scFv expression, and the therapeutic efficacy were assessed.
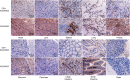
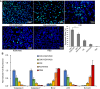
Results: In vitro studies showed that KGHV500 had potent anti-tumor activity. In addition, in vivo, this combination therapy significantly inhibited the growth of lung cancer xenografts compared with mice treated with KGHV500 alone. KGHV500 and anti-p21Ras scFv were observed in tumor tissue, but were nearly undetectable in normal tissues.
Conclusions: The co-delivery of anti-p21Ras scFv by CIK cells and KGHV500 could increase the anti-tumor effect and safety, and possess considerable advantages for the treatment of Ras-related cancer.
Keywords: Adenovirus; Anti-p21Ras scFv; CIK cells; Carrier; Lung cancer; Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Andtbacka RH, Kaufman HL, Collichio F, Amatruda T, Senzer N, Chesney J, Delman KA, Spitler LE, Puzanov I, Agarwala SS (2015) Talimogene laherparepvec improves durable response rate in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol 33(25):2780–2788 - PubMed
-
- Casaluce F, Sgambato A, Sacco PC, Palazzolo G, Maione P, Rossi A, Ciardiello F, Gridelli C (2016) Resistance to crizotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with ALK rearrangement: mechanisms, treatment strategies and new targeted therapies. Curr Clin Pharmacol 11(2):77–87 - PubMed
-
- Crino L, Weder W, van Meerbeeck J, Felip E, Group EGW (2010) Early stage and locally advanced (non-metastatic) non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 5):v103–115 - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386 - PubMed
-
- Finke S, Trojaneck B, Lefterova P, Csipai M, Wagner E, Kircheis R, Neubauer A, Huhn D, Wittig B, Schmidt-Wolf IG (1998) Increase of proliferation rate and enhancement of antitumor cytotoxicity of expanded human CD3 + CD56 + immunologic effector cells by receptor-mediated transfection with the interleukin-7 gene. Gene therapy 5(1):31–39 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

