Neuroimaging of acute and chronic unilateral and bilateral thalamic lesions
- PMID: 30796553
- PMCID: PMC6386756
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-019-0700-3
Neuroimaging of acute and chronic unilateral and bilateral thalamic lesions
Abstract
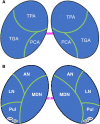
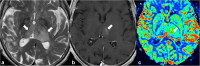
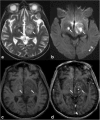
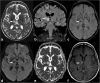
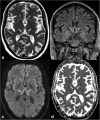
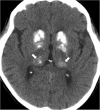
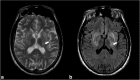
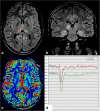
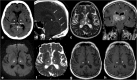
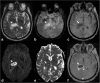
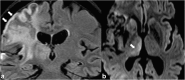
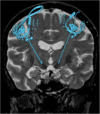
The thalami are bilateral ovoid grey matter cerebral structures bordering the third ventricle on both sides, which participate in functions such as relaying of sensory and motor signals, regulation of consciousness, and alertness. Pathologies affecting the thalami can be of neoplastic, infectious, vascular, toxic, metabolic, or congenital origin.The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive approach to the thalamus focusing on its anatomy, the main pathologies affecting this structure and their radiological semiology on CT and MRI. We will also illustrate the importance of multimodal MR imaging (morphologic sequences, diffusion-weighted imaging, perfusion, spectroscopy) for the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Deep brain stimulation; Infection; Magnetic resonance imaging; Neoplasia; Thalami; Vascular and ischaemic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
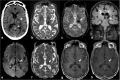
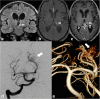
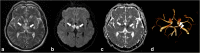
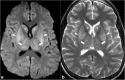
References
-
- Singh V. Textbook of clinical neuroanatomy. Noida: Elsevier; 2004.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

