The estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 is a new putative prognostic biomarker in ER-positive/HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast
- PMID: 30796653
- PMCID: PMC6533234
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-019-05138-7
The estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 is a new putative prognostic biomarker in ER-positive/HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast
Abstract
Purpose: According to the 2017 St Gallen surrogate definitions of the intrinsic subtypes, Ki67, progesterone receptor (PR) and Nottingham histological grade (NHG) are used for prognostic classification of estrogen receptor (ER) positive/HER2-negative breast cancer into luminal A- or luminal B-like. The aim of the present study was to investigate if additional biomarkers, related to endocrine signaling pathways, e.g., amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1), androgen receptor (AR), and G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), can provide complementary prognostic information in a subset of ER-positive/HER-negative invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
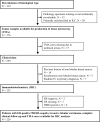
Methods: Biomarkers from 224 patients were analyzed immunohistochemically on tissue microarray. The primary endpoint was breast cancer mortality (BCM), analyzed with 10- and 25-year follow-up (FU). In addition, the prognostic value of gene expression data for these biomarkers was analyzed in three publicly available ILC datasets.
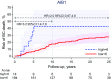
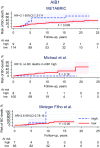
Results: AIB1 (high vs. low) was associated to BCM in multivariable analysis (adjusted for age, tumor size, nodal status, NHG, Ki67, luminal-like classification, and adjuvant systemic therapy) with 10-year FU (HR 6.8, 95% CI 2.3-20, P = 0.001) and 25-year FU (HR 3.0, 95% CI 1.1-7.8, P = 0.03). The evidence of a prognostic effect of AIB1 could be confirmed by linking gene expression data to outcome in independent publicly available ILC datasets. AR and GPER were neither associated to BCM with 10-year nor with 25-year FU (P > 0.33). Furthermore, Ki67 and NHG were prognostic for BCM at both 10-year and 25-year FU, whereas PR was not.
Conclusions: AIB1 is a new putative prognostic biomarker in ER-positive/HER2-negative ILC.
Keywords: Amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1); Androgen receptor (AR); G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER); Gene expression; Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC); Prognostic biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of AIB1 protein as a prognostic factor in breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2011 Oct 29;9:139. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-9-139. World J Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22035181 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and progesterone receptor expression levels do not differ between lobular and ductal carcinoma in patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jul;164(1):133-138. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4220-x. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28365833 Free PMC article.
-
Targetable ERBB2 mutation status is an independent marker of adverse prognosis in estrogen receptor positive, ERBB2 non-amplified primary lobular breast carcinoma: a retrospective in silico analysis of public datasets.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 11;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01324-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32782013 Free PMC article.
-
The role of amplified in breast cancer 1 in breast cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e23248. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023248. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181714 Free PMC article.
-
Triple-negative pleomorphic lobular carcinoma and expression of androgen receptor: Personal case series and review of the literature.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 22;15(7):e0235790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235790. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32697770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AIB1/SRC-3/NCOA3 function in estrogen receptor alpha positive breast cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 30;14:1250218. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1250218. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37711895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prognostic Role of Intratumoral Stromal Content in Lobular Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 14;14(4):941. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040941. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205688 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine resistance in breast cancer: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Dec;99(12):1691-1710. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02136-5. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34623477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARe we there yet? Understanding androgen receptor signaling in breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020 Sep 25;6:47. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00190-9. eCollection 2020. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33062889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AIB1 sequestration by androgen receptor inhibits estrogen-dependent cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 4;19(1):1038. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6262-4. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31684907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Fernandez A, Lain JM, Chabrera C, Garcia Font M, Fraile M, Barco I, Torras M, Rene A, Gonzalez S, Gonzalez C, Piqueras M, Veloso E, Cirera L, Pessarrodona A, Gimenez N. Comparative Long-term Study of a Large Series of Patients with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma and Invasive Lobular Carcinoma. Loco-Regional Recurrence, Metastasis, and Survival. Breast J. 2015;21(5):533–537. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12455. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ (eds) (2012) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast. 4th Edn. WHO press
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

