Immunological pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 30796732
- PMCID: PMC7040062
- DOI: 10.1007/s12519-019-00229-3
Immunological pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE) is a complex and clinically heterogeneous autoimmune disease. A variety of immunological defects contribute to SLE, including dysregulated innate and adaptive immune response. A clearer understanding of the mechanisms driving disease pathogenesis combined with recent advances in medical science is predicted to enable accelerated progress towards improved SLE-personalized approaches to treatment. The aim of this review was to clarify the immunological pathogenesis and treatment of SLE.
Data sources: Literature reviews and original research articles were collected from database, including PubMed and Wanfang. Relevant articles about SLE were included.
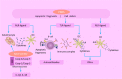
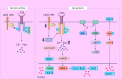
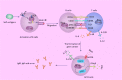
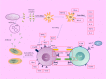
Results: Breakdown of self-tolerance is the main pathogenesis of SLE. The innate and adaptive immune networks are interlinked with each other through cytokines, complements, immune complexes and kinases of the intracellular machinery. Treatments targeted at possible targets of immunity have been assessed in clinical trials. Most of them did not show better safety and efficacy than traditional treatments. However, novel targeting treatments are still being explored.
Conclusions: Dysregulated immune response plays a critical role in SLE, including innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Biologic agents that aim to specifically target abnormal immune processes were assessing and may bring new hope to SLE patients.
Keywords: Immunological pathogenesis; Systemic lupus erythematosis; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose. No financial or nonfinancial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Costa Reis P, Sullivan KE. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:716–730. - PubMed
-
- Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979;301:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Han GM, Chen SL, Shen N, Ye S, Bao CD, Gu YY. Analysis of gene expression profiles in human systemic lupus erythematosus using oligonucleotide microarray. Genes Immun. 2003;4:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Ishii T, Onda H, Tanigawa A, Ohshima S, Fujiwara H, Mima T, et al. Isolation and expression profiling of genes upregulated in the peripheral blood cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. DNA Res. 2005;12:429–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

