Intranasal Losartan Decreases Perivascular Beta Amyloid, Inflammation, and the Decline of Neurogenesis in Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 30796737
- PMCID: PMC6694377
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-019-00723-6
Intranasal Losartan Decreases Perivascular Beta Amyloid, Inflammation, and the Decline of Neurogenesis in Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
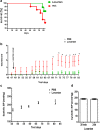
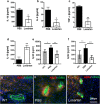
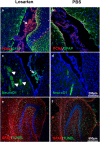
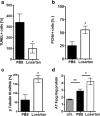
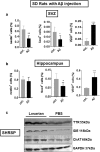
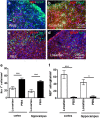
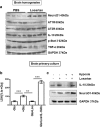
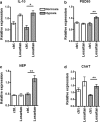
The contribution of the local angiotensin receptor system to neuroinflammation, impaired neurogenesis, and amyloid beta (Aβ) accumulation in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and in hypertension is consistent with the remarkable neuroprotection provided by angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) independent of their blood pressure-lowering effect. Considering the causal relationship between hypertension and AD and that targeting cerebrovascular pathology with ARBs does not necessarily require their systemic effects, we tested intranasal losartan in the rat model of chronic hypertension (spontaneously hypertensive stroke-prone rats, SHRSP). Intranasal losartan at a subdepressor dose decreased mortality, neuroinflammation, and perivascular content of Aβ by enhancing key players in its metabolism and clearance, including insulin-degrading enzyme, neprilysin, and transthyretin. Furthermore, this treatment improved neurologic deficits and increased brain IL-10 concentration, hippocampal cell survival, neurogenesis, and choroid plexus cell proliferation in SHRSP. Losartan (1 μM) also reduced LDH release from cultured astroglial cells in response to toxic glutamate concentrations. This effect was completely blunted by IL-10 antibodies. These findings suggest that intranasal ARB treatment is a neuroprotective, neurogenesis-inducing, and Aβ-decreasing strategy for the treatment of hypertensive stroke and cerebral amyloid angiopathy acting at least partly through the IL-10 pathway.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Angiotensin; Angiotensin receptor blocker; Cerebral amyloid angiopathy; Hemorrhagic stroke; Intranasal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin IV Receptors Mediate the Cognitive and Cerebrovascular Benefits of Losartan in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Neurosci. 2017 May 31;37(22):5562-5573. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0329-17.2017. Epub 2017 May 5. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28476949 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of intranasal losartan in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease.Rejuvenation Res. 2010 Apr-Jun;13(2-3):195-201. doi: 10.1089/rej.2009.0944. Rejuvenation Res. 2010. PMID: 20370487
-
Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer's Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Feb 20;14(2):166. doi: 10.3390/ph14020166. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672482 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the molecular pharmacology of Losartan and its possible relevance to stroke prevention in patients with hypertension.Clin Ther. 2006 Jun;28(6):832-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.06.002. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16860167 Review.
-
Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonism and protection against cardiovascular end-organ damage.J Hum Hypertens. 1998 May;12(5):301-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1000634. J Hum Hypertens. 1998. PMID: 9655651 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of dopaminergic signaling in the cross talk between the renin-angiotensin system and inflammation.Semin Immunopathol. 2020 Dec;42(6):681-696. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00819-8. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Semin Immunopathol. 2020. PMID: 32997225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Injury-Mediated Neuroinflammatory Response and Alzheimer's Disease.Neuroscientist. 2020 Apr;26(2):134-155. doi: 10.1177/1073858419848293. Epub 2019 May 16. Neuroscientist. 2020. PMID: 31092147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Renin-Angiotensin System at the Intersect of Physical and Cognitive Frailty.Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 30;14:586314. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.586314. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33117127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotype Shifting in Astrocytes Account for Benefits of Intra-Arterial Selective Cooling Infusion in Hypertensive Rats of Ischemic Stroke.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Jan;19(1):386-398. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01186-y. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35044645 Free PMC article.
-
Propionic and valproic acids have an impact on bacteria viability, proton flux and ATPase activity.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023 Oct;55(5):397-408. doi: 10.1007/s10863-023-09983-6. Epub 2023 Sep 13. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023. PMID: 37700074
References
-
- Joglar B, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Rey P, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. The inflammatory response in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease is mediated by brain angiotensin: relevance to progression of the disease. J Neurochem. 2009;109:656–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05999.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

