A Model Information Management Plan for Molecular Pathology Sequence Data Using Standards: From Sequencer to Electronic Health Record
- PMID: 30797065
- PMCID: PMC6521887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2018.12.002
A Model Information Management Plan for Molecular Pathology Sequence Data Using Standards: From Sequencer to Electronic Health Record
Abstract
Incorporating genetic variant data into the electronic health record (EHR) in discrete computable fashion has vexed the informatics community for years. Genetic sequence test results are typically communicated by the molecular laboratory and stored in the EHR as textual documents. Although text documents are useful for human readability and initial use, they are not conducive for data retrieval and reuse. As a result, clinicians often struggle to find historical gene sequence results on a series of oncology patients within the EHR that might influence the care of the current patient. Second, identification of patients with specific mutation results in the EHR who are now eligible for new and/or changing therapy is not easily accomplished. Third, the molecular laboratory is challenged to monitor its sequencing processes for nonrandom process variation and other quality metrics. A novel approach to address each of these issues is presented and demonstrated. The authors use standard Health Level 7 laboratory result message formats in conjunction with international standards, Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms and Human Genome Variant Society nomenclature, to represent, communicate, and store discrete gene sequence data within the EHR in a scalable fashion. This information management plan enables the support of the clinician at the point of care, enhances population management, and facilitates audits for maintaining laboratory quality.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



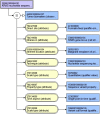
Comment in
-
Expanding the Scope of The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics to the Informatics Subdivision of the Association for Molecular Pathology.J Mol Diagn. 2019 Jul;21(4):539-541. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.04.001. J Mol Diagn. 2019. PMID: 31230765
References
-
- Barnett G.O., Barry M.J., Robb-Nicholson C., Morgan M. Overcoming information overload: an information system for the primary care physician. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2004;107:273–276. - PubMed
-
- Putre L. Personalized medicine. Getting genomic data into EMRs proves challenging. Hosp Health Netw. 2009;83 20,22. - PubMed
-
- Sax U., Schmidt S. Integration of genomic data in Electronic Health Records--opportunities and dilemmas. Methods Inf Med. 2005;44:546–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

