Risk of subsequent primary neoplasms in survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer (Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study): a population-based, cohort study
- PMID: 30797674
- PMCID: PMC6494975
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30903-3
Risk of subsequent primary neoplasms in survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer (Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study): a population-based, cohort study
Abstract
Background: Few studies have investigated the risks of subsequent primary neoplasms after adolescent and young adult (AYA) cancer. We investigated the risks of specific subsequent primary neoplasms after each of 16 types of AYA cancer.
Methods: The Teenage and Young Adult Cancer Survivor Study is a population-based cohort of 200 945 survivors of cancer diagnosed when aged 15-39 years in England and Wales from Jan 1, 1971, to Dec 31, 2006. The cohort was established using cancer registrations from the Office for National Statistics and the Welsh Cancer registry. Follow-up was from 5-year survival until the first occurrence of death, emigration, or study end date (Dec 31, 2012). In this analysis, we focus on the risk of specific subsequent primary neoplasms after 16 types of AYA cancer: breast; cervical; testicular; Hodgkin lymphoma (female); Hodgkin lymphoma (male); melanoma; CNS (intracranial); colorectal; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; thyroid; soft-tissue sarcoma; ovarian; bladder; other female genital; leukaemia; and head and neck cancer. We report absolute excess risks (AERs; per 10 000 person-years) and cumulative incidence of specific types of subsequent primary neoplasm after each type of AYA cancer.
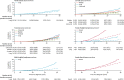
Findings: During the 2 631 326 person-years of follow-up (median follow-up 16·8 years, IQR 10·5-25·2), 12 321 subsequent primary neoplasms were diagnosed in 11 565 survivors, most frequently among survivors of breast cancer, cervical cancer, testicular cancer, and Hodgkin lymphoma. AERs of any subsequent primary neoplasms were 19·5 per 10 000 person-years (95% CI 17·4-21·5) in survivors of breast cancer, 10·2 (8·0-12·4) in survivors of cervical cancer, 18·9 (16·6-21·1) in survivors of testicular cancer, 55·7 (50·4-61·1) in female survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma, and 29·9 (26·3-33·6) in male survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma. The cumulative incidence of all subsequent primary neoplasms 35 years after diagnosis was 11·9% (95% CI 11·3-12·6) in survivors of breast cancer, 15·8% (14·8-16·7) in survivors of cervical cancer, 20·2% (18·9-21·5) in survivors of testicular cancer, 26·6% (24·7-28·6) in female survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma, and 16·5% (15·2-18·0) in male survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma. In patients who had survived at least 30 years from diagnosis of cervical cancer, testicular cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma in women, breast cancer, and Hodgkin lymphoma in men, we identified a small number of specific subsequent primary neoplasms that account for 82%, 61%, 58%, 45%, and 41% of the total excess number of neoplasms, respectively. Lung cancer accounted for a notable proportion of the excess number of neoplasms across all AYA groups investigated.
Interpretation: Our finding that a small number of specific subsequent primary neoplasms account for a large percentage of the total excess number of neoplasms in long-term survivors of cervical, breast, and testicular cancer, and Hodgkin lymphoma provides an evidence base to inform priorities for clinical long-term follow-up. The prominence of lung cancer after each of these AYA cancers indicates the need for further work aimed at preventing and reducing the burden of this cancer in future survivors of AYA cancer.
Funding: Cancer Research UK, National Institute for Health Research, Academy of Medical Sciences, and Children with Cancer UK.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Adolescents and young adults with cancer and the risk of subsequent primary neoplasms: not just big children.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Apr;20(4):466-467. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30941-0. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30797675 No abstract available.
References
-
- Trama A, Botta L, Foschi R. Survival of European adolescents and young adults diagnosed with cancer in 2000–07: population-based data from EUROCARE-5. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:896–906. - PubMed
-
- Aben KK, van Gaal C, van Gils NA, van der Graaf WT, Zielhuis GA. Cancer in adolescents and young adults (15-29 years): a population-based study in the Netherlands 1989-2009. Acta Oncol. 2012;51:922–933. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, DuBois SG, Coccia PF, Bleyer A, Olin RL, Goldsby RE. Increased risk of second malignant neoplasms in adolescents and young adults with cancer. Cancer. 2016;122:116–123. - PubMed
-
- Brown LM, Chen BE, Pfeiffer RM. Risk of second non-hematological malignancies among 376 825 breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106:439–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials