The Wnt inhibitor Dkk1 is required for maintaining the normal cardiac differentiation program in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 30797757
- PMCID: PMC6496975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.02.009
The Wnt inhibitor Dkk1 is required for maintaining the normal cardiac differentiation program in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
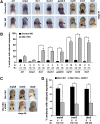
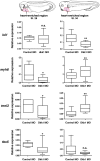
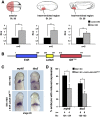
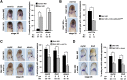
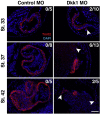
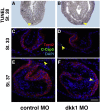
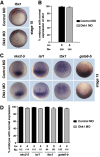
Wnt proteins can activate different intracellular signaling pathways. These pathways need to be tightly regulated for proper cardiogenesis. The canonical Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor Dkk1 has been shown to be sufficient to trigger cardiogenesis in gain-of-function experiments performed in multiple model systems. Loss-of-function studies however did not reveal any fundamental function for Dkk1 during cardiogenesis. Using Xenopus laevis as a model we here show for the first time that Dkk1 is required for proper differentiation of cardiomyocytes, whereas specification of cardiomyocytes remains unaffected in absence of Dkk1. This effect is at least in part mediated through regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling via Wnt11. In line with these observations we also found that Isl1, a critical regulator for specification of the common cardiac progenitor cell (CPC) population, acts upstream of Dkk1.
Keywords: Cardiac differentiation; dkk1; isl1.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Wnt5a and Wnt11 interact in a maternal Dkk1-regulated fashion to activate both canonical and non-canonical signaling in Xenopus axis formation.Development. 2008 Nov;135(22):3719-29. doi: 10.1242/dev.029025. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Development. 2008. PMID: 18927149
-
The CapZ interacting protein Rcsd1 is required for cardiogenesis downstream of Wnt11a in Xenopus laevis.Dev Biol. 2017 Apr 1;424(1):28-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.02.014. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28237811
-
Dickkopf-1 regulates gastrulation movements by coordinated modulation of Wnt/beta catenin and Wnt/PCP activities, through interaction with the Dally-like homolog Knypek.Genes Dev. 2007 Feb 15;21(4):465-80. doi: 10.1101/gad.406007. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17322405 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal control of pattern formation in Xenopus laevis.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2008 Jan 15;310(1):73-84. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.21153. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2008. PMID: 17219372 Review.
-
Cadherins and catenins, Wnts and SOXs: embryonic patterning in Xenopus.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;203:291-355. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)03010-8. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11131519 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Methylation in Determining the Fate of Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Sep 22;2022:5015856. doi: 10.1155/2022/5015856. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 36187229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the latest advancements in cardiac regeneration using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) technology: approaches and challenges.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 22;22(1):783. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05499-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39175068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac stem cells: Current knowledge and future prospects.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Jan 26;14(1):1-40. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.1. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35126826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
γ-catenin alleviates cardiac fibrosis through inhibiting phosphorylation of GSK-3β.J Biomed Res. 2019 Jul 30;0(0):1-9. doi: 10.7555/JBR.33.20190070. J Biomed Res. 2019. PMID: 31741464 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effects of three neonicotinoids on embryogenesis of the South African clawed frog Xenopus laevis.Curr Res Toxicol. 2024 Apr 21;6:100169. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2024.100169. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38706785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afouda B.A., Hoppler S. Different requirements for GATA factors in cardiogenesis are mediated by non-canonical Wnt signaling. Dev. Dynam. offic. Publ. Am. Associat. Anatomists. 2011;240:649–662. - PubMed
-
- Afouda B.A., Martin J., Liu F., Ciau-Uitz A., Patient R., Hoppler S. GATA transcription factors integrate Wnt signalling during heart development. Development. 2008;135:3185–3190. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J., von Kries J.P., Kühl M., Bruhn L., Wedlich D., Grosschedl R., Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

