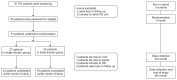
Efficacy of triple diuretic treatment in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30798586
- PMCID: PMC6481970
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.18.0115
Efficacy of triple diuretic treatment in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of combined diuretic treatment in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) is not known.
Methods: In a single-center, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial, we randomly assigned 51 adult CAPD patients to receive furosemide 1,000 mg/day, hydrochlorothiazide 100 mg/day, and spironolactone 50 mg/day (triple diuretics [TD] group) or furosemide 1,000 mg/day plus placebo (single diuretic [SD] group) for 6 months. The primary outcome was the difference in daily urine output at the 3rd and 6th month of the study compared to baseline (ΔUO) between the SD and TD group. Secondary outcomes were urinary sodium (UNa) and potassium (UK) excretion and overhydration (OH) measured by bioimpedance at 3 and 6 months compared to baseline (ΔUNa, ΔUK, and ΔOH, respectively) and daily glucose exposure (g/day).
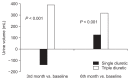
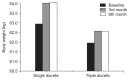
Results: Forty-three of 51 patients completed the 6-month trial. The ΔUO at 3 and 6 months was significantly higher in the TD group compared to the SD group (386.32 ± 733.92 mL/day vs. -136.25 ± 629.08 mL/day, P < 0.001, at 3 months; 311.58 ± 640.31 mL/day vs. 120.00 ± 624.07 mL/day, P < 0.001, at 6 months) but there was no significant difference in ΔUNa and ΔUK excretion. Hydration status was significantly better in the TD group (ΔOH 1.84 ± 2.27 L vs. 0.44 ± 1.62 L, P = 0.03, at 3 months; 1.49 ± 2.82 L vs. -0.48 ± 2.61 L, P = 0.02, at 6 months). There was no serious adverse event in this study.
Conclusion: For end-stage renal disease patients on CAPD, the combination of furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, and spironolactone results in higher urine output and better volume control compared to furosemide alone.
Keywords: Furosemide; Hydration status; Hydrochlorothiazide; Peritoneal dialysis; Spironolactone.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Lameire N, Van Biesen W. Hypervolemia in peritoneal dialysis patients. J Nephrol. 2004;17(Suppl 8):S58–S66. - PubMed
-
- Moist LM, Port FK, Orzol SM, et al. Predictors of loss of residual renal function among new dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11:556–564. - PubMed
-
- Rastogi SP, Volans G, Elliott RW, et al. High dose frusemide in the treatment of hypertension in chronic renal insufficiency and of terminal renal failure. Postgrad Med J. 1971;47(Suppl):45–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

