Acetylation Blocks cGAS Activity and Inhibits Self-DNA-Induced Autoimmunity
- PMID: 30799039
- PMCID: PMC8274936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.016
Acetylation Blocks cGAS Activity and Inhibits Self-DNA-Induced Autoimmunity
Abstract
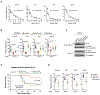
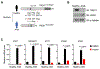
The presence of DNA in the cytoplasm is normally a sign of microbial infections and is quickly detected by cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) to elicit anti-infection immune responses. However, chronic activation of cGAS by self-DNA leads to severe autoimmune diseases for which no effective treatment is available yet. Here we report that acetylation inhibits cGAS activation and that the enforced acetylation of cGAS by aspirin robustly suppresses self-DNA-induced autoimmunity. We find that cGAS acetylation on either Lys384, Lys394, or Lys414 contributes to keeping cGAS inactive. cGAS is deacetylated in response to DNA challenges. Importantly, we show that aspirin can directly acetylate cGAS and efficiently inhibit cGAS-mediated immune responses. Finally, we demonstrate that aspirin can effectively suppress self-DNA-induced autoimmunity in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) patient cells and in an AGS mouse model. Thus, our study reveals that acetylation contributes to cGAS activity regulation and provides a potential therapy for treating DNA-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Aicardi-Goutiéres syndrome; Trex1; acetylation; aspirin; autoimmune disease; cGAS; interferonopathies.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
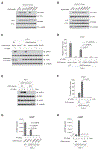
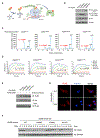
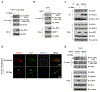

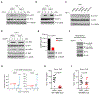
Comment in
-
Aspirin meets cGAS.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 May;15(5):254-255. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0205-y. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30914774 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahn J, and Barber GN (2014). Self-DNA, STING-dependent signaling and the origins of autoinflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol 31, 121–126. - PubMed
-
- Aicardi J, and Goutières F (1984). A progressive familial encephalopathy in infancy with calcifications of the basal ganglia and chronic cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytosis. Ann. Neurol 15, 49–54. - PubMed
-
- An J, Woodward JJ, Sasaki T, Minie M, and Elkon KB (2015). Cutting edge: Antimalarial drugs inhibit IFN-β production through blockade of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-DNA interaction. J. Immunol 194, 4089–4093. - PubMed
-
- Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, and Barton GM (2011). Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol 29, 185–214. - PubMed
-
- Bowie A (2012). The STING in the tail for cytosolic DNA-dependent activation of IRF3. Sci. Signal 5, pe9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

