Genital Infiltrations of CD4+ and CD8+ T Lymphocytes, IgA+ and IgG+ Plasma Cells and Intra-Mucosal Lymphoid Follicles Associate With Protection Against Genital Chlamydia trachomatis Infection in Minipigs Intramuscularly Immunized With UV-Inactivated Bacteria Adjuvanted With CAF01
- PMID: 30800114
- PMCID: PMC6375829
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00197
Genital Infiltrations of CD4+ and CD8+ T Lymphocytes, IgA+ and IgG+ Plasma Cells and Intra-Mucosal Lymphoid Follicles Associate With Protection Against Genital Chlamydia trachomatis Infection in Minipigs Intramuscularly Immunized With UV-Inactivated Bacteria Adjuvanted With CAF01
Abstract
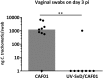
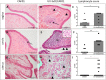
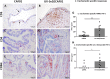
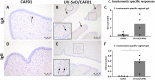
The development of a vaccine against genital chlamydia in women is advancing, and the evaluation of in situ immune responses following vaccination and challenge infections is crucial for development of a safe and protective vaccine. This study employs the sexually mature minipig model to characterize the genital in situ immune response to Chlamydia trachomatis infection in pigs previously immunized intramuscularly with UV-inactivated C. trachomatis serovar D (UV-SvD) adjuvanted/formulated with CAF01 adjuvant compared to a CAF01-alone control group. Pigs immunized with UV-SvD were significantly protected against vaginal challenge with C. trachomatis on day 3 post inoculation and showed significantly higher cervical infiltrations of approximately equal numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, and IgG+ and IgA+ plasma cells compared to adjuvant-alone immunized controls. These immunological signatures correspond to findings in mice and are similar to those described in female chlamydia patients. This proves important potential for the pig model in elucidating immunological in situ signatures in future translational research in chlamydia vaccinology.
Keywords: chlamydia; histology; pathology; porcine; vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- Agger E. M., Rosenkrands I., Hansen J., Brahimi K., Vandahl B. S., Aagaard C., et al. (2008). Cationic liposomes formulated with synthetic mycobacterial cordfactor (CAF01): a versatile adjuvant for vaccines with different immunological requirements. PLoS One 3:e3116. 10.1371/journal.pone.0003116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bøje S., Olsen A. W., Erneholm K., Agerholm J. S., Jungersen G., Andersen P., et al. (2015). A multi-subunit Chlamydia vaccine inducing neutralizing antibodies and strong IFN-γ+ CMI responses protects against a genital infection in minipigs. Immunol. Cell Biol. 94 185–195. 10.1038/icb.2015.79 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

