Diagnostic accuracy of a deep learning approach to calculate FFR from coronary CT angiography
- PMID: 30800150
- PMCID: PMC6379239
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.01.010
Diagnostic accuracy of a deep learning approach to calculate FFR from coronary CT angiography
Abstract
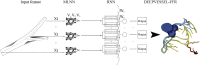
Background: The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) approach has been frequently applied to compute the fractional flow reserve (FFR) using computed tomography angiography (CTA). This technique is efficient. We developed the DEEPVESSEL-FFR platform using the emerging deep learning technique to calculate the FFR value out of CTA images in five minutes. This study is to evaluate the DEEPVESSEL-FFR platform using the emerging deep learning technique to calculate the FFR value from CTA images as an efficient method.
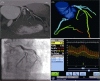
Methods: A single-center, prospective study was conducted and 63 patients were enrolled for the evaluation of the diagnostic performance of DEEPVESSEL-FFR. Automatic quantification method for the three-dimensional coronary arterial geometry and the deep learning based prediction of FFR were developed to assess the ischemic risk of the stenotic coronary arteries. Diagnostic performance of the DEEPVESSEL-FFR was assessed by using wire-based FFR as reference standard. The primary evaluation factor was defined by using the area under receiver-operation characteristics curve (AUC) analysis.
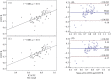
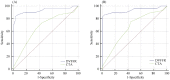
Results: For per-patient level, taking the cut-off value ≤ 0.8 referring to the FFR measurement, DEEPVESSEL-FFR presented higher diagnostic performance in determining ischemia-related lesions with area under the curve of 0.928 compare to CTA stenotic severity 0.664. DEEPVESSEL-FFR correlated with FFR (R = 0.686, P < 0.001), with a mean difference of -0.006 ± 0.0091 (P = 0.619). The secondary evaluation factors, indicating per vessel accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 87.3%, 97.14%, 75%, 82.93%, and 95.45%, respectively.
Conclusion: DEEPVESSEL-FFR is a novel method that allows efficient assessment of the functional significance of coronary stenosis.
Keywords: Computed tomography angiography; Coronary artery; Deep learning; Fractional flow reserve.
Figures
References
-
- Pijls NHJ, Fearon WF, Tonino PA, et al. Fractional flow reserve versus angiography for guiding percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease: 2-year follow-up of the FAME (Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:177–184. - PubMed
-
- Vanhoenacke PK, Heijenbrok-Kal MH, Van Heste R, et al. Diagnostic performance of multidetector CT angiography for assessment of coronary artery disease: meta-analysis. Radiology. 2007;244:419–428. - PubMed
-
- Nørgaard B.L., Leipsic J, Gaur S, et al. Diagnostic performance of noninvasive fractional flow reserve derived from coronary computed tomography angiography in suspected coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1145–1155. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
