Curcumin Suppresses Hepatic Stellate Cell-Induced Hepatocarcinoma Angiogenesis and Invasion through Downregulating CTGF
- PMID: 30800209
- PMCID: PMC6360067
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8148510
Curcumin Suppresses Hepatic Stellate Cell-Induced Hepatocarcinoma Angiogenesis and Invasion through Downregulating CTGF
Abstract
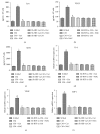
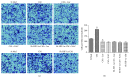
Microenvironment plays a vital role in tumor progression; we focused on elucidating the role of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) in hepatocarcinoma (HCC) aggressiveness and investigated the potential protective effect of curcumin on HSC-driven hepatocarcinoma angiogenesis and invasion. Our data suggest that HSCs increase HCC reactive oxygen species (ROS) production to upregulate hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression to promote angiogenesis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) process and invasion. And HSCs could secrete soluble factors, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), and stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) to facilitate HCC progression. Curcumin could significantly suppress the above HSC-induced effects in HCC and could abrogate ROS and HIF-1α expression in HCC. HIF-1α or connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) knockdown could abolish the aforementioned curcumin affection. Moreover, CTGF is a downstream gene of HIF-1α. In addition, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glutathione (GSH) are involved in curcumin protection of HCC. These data indicate that curcumin may induce ROS scavenging by upregulating Nrf2 and GSH, thus inhibiting HIF-1α stabilization to suppress CTGF expression to exhibit its protection on HCC. Curcumin has a promising therapeutic effect on HCC. CTGF is responsible for curcumin-induced protection in HCC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resveratrol inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression driven by hepatic stellate cells by targeting Gli-1.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Oct;434(1-2):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3031-z. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28455791
-
Canagliflozin Modulates Hypoxia-Induced Metastasis, Angiogenesis and Glycolysis by Decreasing HIF-1α Protein Synthesis via AKT/mTOR Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 11;22(24):13336. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413336. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948132 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting different angiogenic pathways with combination of curcumin, leflunomide and perindopril inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;723:267-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.11.022. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24291100
-
Hypoxia inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12171-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic modulators of hepatic stellate cells for hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2020 Sep 15;147(6):1519-1527. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32899. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32010970 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of exosomes in hepatocellular carcinoma and the regulation of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1110922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1110922. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36733504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying cancer-associated fibroblasts as emerging targets for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Biosci. 2020 Oct 31;10(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00488-y. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33292459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLUD1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via ROS-mediated p38/JNK MAPK pathway activation and mitochondrial apoptosis.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jan 12;15(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00860-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38216781 Free PMC article.
-
A curcumin analog GL63 inhibits the malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma by inactivating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway via the circular RNA zinc finger protein 83/microRNA-324-5p/cyclin-dependent kinase 16 axis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Oct;36(10):2967-2977. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15545. Epub 2021 Jun 3. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33982329 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin inhibited the growth and invasion of human monocytic leukaemia SHI-1 cells in vivo by altering MAPK and MMP signalling.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):25-34. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1701042. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 31854220 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

