Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues
- PMID: 30800295
- PMCID: PMC6359888
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.81.BJR-2018-0181.R1
Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues
Abstract
Objectives: Tranexamic acid (TXA) is an anti-fibrinolytic medication commonly used to reduce perioperative bleeding. Increasingly, topical administration as an intra-articular injection or perioperative wash is being administered during surgery. Adult soft tissues have a poor regenerative capacity and therefore damage to these tissues can be harmful to the patient. This study investigated the effects of TXA on human periarticular tissues and primary cell cultures using clinically relevant concentrations.
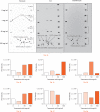
Methods: Tendon, synovium, and cartilage obtained from routine orthopaedic surgeries were used for ex vivo and in vitro studies using various concentrations of TXA. The in vitro effect of TXA on primary cultured tenocytes, fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and chondrocytes was investigated using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) cell viability assays, fluorescent microscopy, and multi-protein apoptotic arrays for cell death.
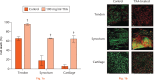
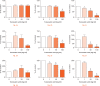
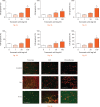
Results: There was a significant (p < 0.01) increase in cell death within all tissue explants treated with 100 mg/ml TXA. MTT assays revealed a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in cell viability in all tissues following treatment with 50 mg/ml or 100 mg/ml of TXA within four hours. There was a significant (p < 0.05) increase in cell apoptosis after one hour of exposure to TXA (100 mg/ml) in all tissues.
Conclusion: The current study demonstrates that TXA caused significant periarticular tissue toxicity ex vivo and in vitro at commonly used clinical concentrations.Cite this article: M. McLean, K. McCall, I. D. M. Smith, M. Blyth, S. M. Kitson, L. A. N. Crowe, W. J. Leach, B. P. Rooney, S. J. Spencer, M. Mullen, J. L. Campton, I. B. McInnes, M. Akbar, N. L. Millar. Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues. Bone Joint Res 2019;8:11-18. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.81.BJR-2018-0181.R1.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cartilage; Periarticular tissues; Synovium; Tendon; Tranexamic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: None declared
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of tranexamic acid on synovium of patients undergoing arthroplasty and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;396(12):3733-3742. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02555-w. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37318523
-
Toxicity of tranexamic acid (TXA) to intra-articular tissue in orthopaedic surgery: a scoping review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Jun;29(6):1862-1871. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06219-7. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32860523
-
Cytotoxicity of tranexamic acid to tendon and bone in vitro: Is there a safe dosage?J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 May 15;17(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03167-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35570313 Free PMC article.
-
Is tranexamic acid toxic to articular cartilage when administered topically? What is the safe dose?Bone Joint J. 2018 Mar 1;100-B(3):404-412. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B3.BJJ-2017-1135.R1. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29589496
-
Topical use of tranexamic acid: Are there concerns for cytotoxicity?World J Orthop. 2022 Jun 18;13(6):555-563. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i6.555. eCollection 2022 Jun 18. World J Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35949709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Use of Tranexamic Acid and Rivaroxaban in Posterior/Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgeries Safely Reduces Blood Loss and Incidence of Thrombosis: Evidence From a Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study.Global Spine J. 2023 Jun;13(5):1229-1237. doi: 10.1177/21925682211024556. Epub 2021 Sep 26. Global Spine J. 2023. PMID: 34569334 Free PMC article.
-
[Early effectiveness of local injection of multimodal drug cocktail during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and its influence on cartilage].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;38(5):562-569. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202402054. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38752242 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Peri-articular administration of tranexamic acid is an alternative route in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Apr 7;17(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03095-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35392961 Free PMC article.
-
Short exposure to tranexamic acid does not affect, in vitro, the viability of human chondrocytes.Eur J Med Res. 2019 Feb 22;24(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0373-x. Eur J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30795796 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of tranexamic acid on synovium of patients undergoing arthroplasty and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;396(12):3733-3742. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02555-w. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37318523
References
-
- Neveleff DJ, Kraiss LW, Schulman CS. Implementing methods to improve perioperative hemostasis in the surgical and trauma settings. AORN J 2010;92:S1-S15. - PubMed

