Identification of copper (Cu) stress-responsive grapevine microRNAs and their target genes by high-throughput sequencing
- PMID: 30800341
- PMCID: PMC6366190
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.180735
Identification of copper (Cu) stress-responsive grapevine microRNAs and their target genes by high-throughput sequencing
Abstract
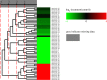
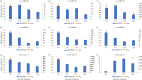
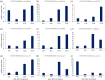
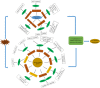
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of single-stranded non-coding small RNAs (sRNAs) that are 20-24 nucleotides (nt) in length. Extensive studies have indicated that miRNAs play important roles in plant growth, development and stress responses. With more copper (Cu) and copper containing compounds used as bactericides and fungicides in plants, Cu stress has become one of the serious environmental problems that affect plant growth and development. In order to uncover the hidden response mechanisms of Cu stress, two small RNA libraries were constructed from Cu-treated and water-treated (Control) leaves of 'Summer Black' grapevine. Following high-throughput sequencing and filtering, a total of 158 known and 98 putative novel miRNAs were identified in the two libraries. Among these, 100 known and 47 novel miRNAs were identified as differentially expressed under Cu stress. Subsequently, the expression patterns of nine Cu-responsive miRNAs were validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). There existed some consistency in expression levels of Cu-responsive miRNAs between high throughput sequencing and qRT-PCR assays. The targets prediction of miRNAs indicates that miRNA may regulate some transcription factors, including AP2, SBP, NAC, MYB and ARF during Cu stress. The target genes for two known and two novel miRNAs showed specific cleavage sites at the 10th and/or 11th nucleotide from the 5'-end of the miRNA corresponding to their miRNA complementary sequences. The findings will lay the foundation for exploring the role of the regulation of miRNAs in response to Cu stress and provide valuable gene information for breeding some Cu-tolerant grapevine cultivars.
Keywords: Cu stress; grapevine; high-throughput sequencing; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of chilling stress-responsive tomato microRNAs and their target genes by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 17;15(1):1130. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1130. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25519760 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and identification of grapevine heat stress-responsive microRNAs revealed the positive regulated function of vvi-miR167 in thermostability.Plant Sci. 2023 Apr;329:111623. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111623. Epub 2023 Feb 5. Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36750140
-
Identification of cold-inducible microRNAs in grapevine.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Aug 4;6:595. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00595. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26300896 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of low phosphorus responsive microRNAs in two soybean genotypes by high-throughput sequencing.Funct Integr Genomics. 2020 Nov;20(6):825-838. doi: 10.1007/s10142-020-00754-9. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33009591
-
Regulatory role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the recent development of abiotic stress tolerance of plants.Gene. 2022 May 5;821:146283. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146283. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35143944 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-124: An emerging therapeutic target in cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(12):5638-5650. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2489. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31389160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA gatekeepers: Orchestrating rhizospheric dynamics.J Integr Plant Biol. 2025 Mar;67(3):845-876. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13860. Epub 2025 Feb 21. J Integr Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39981727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The grapevine miR827a regulates the synthesis of stilbenes by targeting VqMYB14 and gives rise to susceptibility in plant immunity.Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Apr 6;137(4):95. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04599-9. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38582777
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Copper Stress-Regulated and Novel MicroRNAs in Mulberry Leaf.Biochem Genet. 2021 Apr;59(2):589-603. doi: 10.1007/s10528-020-10021-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Biochem Genet. 2021. PMID: 33389282
-
Small RNA profiling reveals the involvement of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in response to symbiosis in raspberry.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1082494. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1082494. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36620006 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

