Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacterium Bacillus aryabhattai from pulp and paper mill wastewater and evaluation of its lignin-degrading potential
- PMID: 30800603
- PMCID: PMC6385068
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1631-x
Isolation and characterization of lignin-degrading bacterium Bacillus aryabhattai from pulp and paper mill wastewater and evaluation of its lignin-degrading potential
Abstract
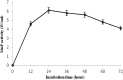
This study reports the degradation and decolourization capability of a manganese peroxidase enzyme producing bacterium isolated from pulp and paper mill wastewater. The isolate was identified as Bacillus aryabhattai based on biochemical analysis and 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The strain was designated MG966493. This bacterium was able to reduce 67% and 54% colour and lignin, respectively, from the pulp and paper mill wastewater after 144 h of treatment at 32 °C, pH 7.6 and 120 rpm. Further, FT-IR analysis showed that during the lignin degradation process a number of metabolites were produced comprising different functional groups such as carbonyl (C=C), carboxyl (-COOH), alkene (C=C), amines (-NH2), sulphonic (-SO3) and nitro (-NO2). In addition, the SEM analysis showed that the bacterial cells exposed to pulp and paper mill wastewater have rough surfaces with reduced size as compared to the unexposed cells with smooth surfaces. This study concluded that the isolated bacterium B. aryabhattai has significant potential for the bioremediation of pulp and paper mill wastewater and thus, can be applied for their treatment at an industrial scale.
Keywords: Bacterial degradation; FT-IR analysis; Lignin reduction; Pulp and paper mill wastewater; SEM analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Ali M, Sreekrishnan TR. Aquatic toxicity from pulp and paper mill effluents: a review. Adv Environ Res. 2001;5:175–196. doi: 10.1016/S1093-0191(00)00055-1. - DOI
-
- APHA . Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewaters. 22. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environmental Federation; 2012. p. 981.
-
- Atashpaz S, Barzegari AK, Barar J, Vahed SZ, Azarbaijani R, Omidi Y. A robust universal method for the extraction of genomic, DNA Bact. Species Microbiol. 2010;79(4):562–566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

