Trends in Diagnostics, Surgical Treatment, and Prognostic Factors for Outcomes in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in Norway: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- PMID: 30800639
- PMCID: PMC6381913
- DOI: 10.1159/000493977
Trends in Diagnostics, Surgical Treatment, and Prognostic Factors for Outcomes in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma in Norway: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is rare. Nationwide population-based studies are important to evaluate its clinical course.
Objectives: To describe all patients with MTC in Norway during 1994-2016 and compare time-related trends in diagnostics and surgical treatment, including prognostic factors for biochemical cure and disease-specific survival (DSS).
Methods: This retrospective population-based cohort study includes data for 228 out of 237 patients (96%) with MTC; 201 patients were surgically treated. Patients were identified in the 4 regional centers treating MTC and by the Cancer Registry of Norway. Data were collected from patients' files. Trends were compared over 2 study periods.
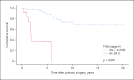
Results: MTC accounted for 4.2% of thyroid carcinomas. During the study periods, the incidence increased from 0.18 to 0.25: 100,000 per year, preoperative diagnostics improved with increased use of calcitonin, ultrasound, and fine-needle cytology (p = 0.010, p < 0,001, and p = 0.001), patients were diagnosed at an earlier tumor stage (p = 0.004), and more patients were cured (p = 0.002). Via multivariate analysis of patients with metastatic lymph nodes, independent prognostic factors for cure were: a low ratio of metastatic and total number of dissected lymph nodes (p = 0.021) and no extrathyroidal extension (p = 0.030). Independent prognostic factors for DSS were: no distant metastasis, a younger age, and a low ratio of metastatic and dissected lymph nodes (p = 0.005, p = 0.020, p = 0.022).
Conclusions: Preoperative diagnostics have improved over time with increased therapeutic control. A low ratio of metastatic and dissected lymph nodes predicts better outcomes in patients with metastatic lymph nodes.
Keywords: Diagnostics; Medullary thyroid carcinoma; Outcome; Pathology; Surgery; Trends.
Figures
References
-
- Kebebew E, Ituarte PH, Siperstein AE, Duh QY, Clark OH. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: clinical characteristics, treatment, prognostic factors, and a comparison of staging systems. Cancer. 2000 Mar;88((5)):1139–48. - PubMed
-
- Akslen LA, Haldorsen T, Thoresen SO, Glattre E. Incidence of thyroid cancer in Norway 1970-1985. Population review on time trend, sex, age, histological type and tumour stage in 2625 cases. APMIS. 1990 Jun;98((6)):549–58. - PubMed
-
- Pelizzo MR, Boschin IM, Bernante P, Toniato A, Piotto A, Pagetta C. Natural history, diagnosis, treatment and outcome of medullary thyroid cancer: 37 years experience on 157 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007 May;33((4)):493–7. - PubMed
-
- Donis-Keller H, Dou S, Chi D, Carlson KM, Toshima K, Lairmore TC. Mutations in the RET proto-oncogene are associated with MEN 2A and FMTC. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2((7)):851–6. - PubMed