Transmembrane protein 100 is expressed in neurons and glia of dorsal root ganglia and is reduced after painful nerve injury
- PMID: 30801043
- PMCID: PMC6370145
- DOI: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000703
Transmembrane protein 100 is expressed in neurons and glia of dorsal root ganglia and is reduced after painful nerve injury
Abstract
Introduction: Tmem100 modulates interactions between TRPA1 and TRPV1. The cell specificity of Tmem100 expression in dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) is not well defined, nor is the effect of peripheral nerve injury on Tmem100 expression.
Objective: This study was designed to determine the cell specificity of Tmem100 expression in DRG and its subcellular localization, and to examine how Tmem100 expression may be altered in painful conditions.
Methods: Dorsal root ganglion Tmem100 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry, immunoblot, and quantitative real-time PCR, and compared between various experimental rat pain models and controls.
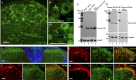
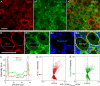
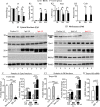
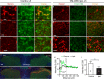
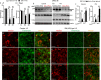
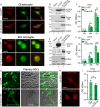
Results: Tmem100 is expressed in both neurons and perineuronal glial cells in the rat DRG. The plasma membrane and intracellular localization of Tmem100 are identified in 83% ± 6% of IB4-positive and 48% ± 6% of calcitonin gene-related peptide-positive neurons, as well as in medium- and large-sized neurons, with its immunopositivity colocalized to TRPV1 (94% ± 5%) and TRPA1 (96% ± 3%). Tmem100 is also detected in the perineuronal satellite glial cells and in some microglia. Tmem100 protein is significantly increased in the lumbar DRGs in the complete Freund adjuvant inflammatory pain. By contrast, peripheral nerve injury by spinal nerve ligation diminishes Tmem100 expression in the injured DRG, with immunoblot and immunohistochemistry experiments showing reduced Tmem100 protein levels in both neurons and satellite glial cells of DRGs proximal to injury, whereas Tmem100 is unchanged in adjacent DRGs. The spared nerve injury model also reduces Tmem100 protein in the injured DRGs.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate a pain pathology-dependent alteration of DRG Tmem100 protein expression, upregulated during CFA inflammatory pain but downregulated during neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Dorsal root ganglia; Inflammatory pain; Microglia; Neuropathic pain; Primary sensory neurons; Satellite glial cells; Transmembrane protein 100.
Conflict of interest statement
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Aoki Y, Ohtori S, Takahashi K, Ino H, Takahashi Y, Chiba T, Moriya H. Innervation of the lumbar intervertebral disc by nerve growth factor-dependent neurons related to inflammatory pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:1077–81. - PubMed
-
- Bailey AL, Ribeiro-da-Silva A. Transient loss of terminals from non-peptidergic nociceptive fibers in the substantia gelatinosa of spinal cord following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Neuroscience 2006;138:675–90. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
