Is It Possible to Correct Congenital Spinal Deformity Associated With a Tethered Cord Without Prophylactic Intradural Detethering?
- PMID: 30801282
- PMCID: PMC6999982
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000652
Is It Possible to Correct Congenital Spinal Deformity Associated With a Tethered Cord Without Prophylactic Intradural Detethering?
Abstract
Background: Patients who have a congenital spinal deformity with a tethered cord generally are treated with prophylactic intradural detethering before deformity correction. However, the detethering procedure carries substantial risk, and it is not clear whether deformity correction can be performed without detethering.
Questions/purposes: To determine the (1) correction rate, (2) proportion of patients who experienced complications after surgery, and (3) neurological status after recovery from surgery in a group of patients with congenital spinal deformity and a tethered cord who were treated either with posterior spinal fusion only (PSF), pedicle-subtraction osteotomy (PSO), or a vertebral column resection (VCR), based on an algorithmic approach.
Methods: Between 2006 and 2016, we treated 50 patients surgically for a congenital spinal deformity and a tethered cord. We defined a congenital spinal deformity as one that was caused by failure of vertebral segmentation, failure of vertebral formation, or both, and we made the diagnosis of a tethered cord based on a conus medullaris lower than L2 level, or a diameter of the filum terminale greater than 2 mm, as shown on magnetic resonance image. Of those, nine patients were lost to followup before the 2-year minimum, leaving 41 for analysis at a mean followup of 47 months (range, 24 to 92 months) in this single-institution retrospective study. The treatment algorithm involved one of three approaches: PSF, PSO, or VCR. A total of 15 patients underwent PSF; we used this approach for patients with moderate curves (Cobb angle < 80°) and intact neurological status both previously and during a bending and traction test. Eleven patients underwent PSO; we performed PSO when patients had neurological symptoms (in daily life or during the traction/bending test) and a magnitude of the curve less than 80°. Finally, 15 patients underwent VCR, which we used in patients with a magnitude of the curve more than 80° and/or flexibility less than 20%, with/without neurological symptoms. No patient in any group underwent intradural detethering. We report on the correction rate, defined as the ratio between the corrected magnitude and preoperative magnitude of a curve at a given postoperative time point (correction rate = 1- (Cobb angle at a given time point/preoperative Cobb angle) x 100%); complications, that is, postoperative/recurrent neurological symptoms, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, infection, blood loss > 5000 mL, as determined by chart review performed by an individual not directly involved in patient care; and a detailed neurological exam, including evaluations of sensory function, extremity muscle strength, pain, gait, physiological reflexes, and pathological signs, both before surgery and at most recent followup, as performed by the surgeon. All neurologically symptomatic patients were evaluated with a neurologic scoring system.
Results: The overall mean ± SD correction rate in this series was 63% ± 14%. It was 70% ± 12% in the PSF group, 64% ± 17% in the PSO group, and 56% ± 12% in the VCR group. Seven patients in those three groups experienced major complications, including blood loss more than 5000 mL, temporary neurological symptoms, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, and infection. The most severe complications included one patient in the VCR group who had temporarily decreased strength in the lower limb, and one patient in the PSO group with temporary numbness in the lower limb. Finally, no patients in PSF group had postoperative neurological complications, and all patients with neurological symptoms in the PSO/VCR group improved to varying degrees. For neurologically symptomatic patients in PSO group (n = 6), the neurological score improved slightly, from 22.5 ± 1.9 preoperatively to 24.2 ± 0.8 at the most recent followup (p = 0.024) with a mean difference of 1.7. For neurologically symptomatic patients in VCR group (n = 10), the neurological score improved slightly from 23.1 ± 1.1 preoperatively to 24.2 ± 0.6 at most recent followup (p = 0.009) with a mean difference of 1.1.
Conclusions: Congenital spinal deformity with a tethered cord may be treated without prophylactic intradural detethering. In the current series treated according to this treatment algorithm, good correction and neurological improvement were achieved, and few complications occurred. However, such a small series cannot prove the safety of this treatment; for that, larger, multicenter studies are necessary.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures
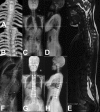
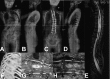
Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: Is It Possible to Correct Congenital Spinal Deformity Associated With a Tethered Cord Without Prophylactic Intradural Detethering?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Jul;477(7):1698-1699. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000709. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31107328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Is detethering necessary before deformity correction in congenital scoliosis associated with tethered cord syndrome: a meta-analysis of current evidence.Eur Spine J. 2021 Mar;30(3):599-611. doi: 10.1007/s00586-020-06662-7. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Eur Spine J. 2021. PMID: 33201289
-
Surgical Treatment of Congenital Scoliosis Associated With Tethered Cord by Thoracic Spine-shortening Osteotomy Without Cord Detethering.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015 Oct 15;40(20):E1103-9. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001035. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015. PMID: 26110661
-
Corrective Surgery for Congenital Scoliosis Associated with Split Cord Malformation: It May Be Safe to Leave Diastematomyelia Untreated in Patients with Intact or Stable Neurological Status.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016 Jun 1;98(11):926-36. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.15.00882. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016. PMID: 27252437
-
Comparison of Perioperative Complication Rates in Congenital Scoliosis Patients With and Without Tethered Spinal Cord.J Pediatr Orthop. 2025 Apr 1;45(4):e352-e357. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002883. Epub 2024 Dec 24. J Pediatr Orthop. 2025. PMID: 39716830
-
Treatment of spinal deformity with diastematomyelia type I: one-stage, two-stage surgery and new technique (vertebral column resection through wide bony septum).Childs Nerv Syst. 2022 Jan;38(1):163-172. doi: 10.1007/s00381-021-05382-7. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Childs Nerv Syst. 2022. PMID: 34626222 Review.
Cited by
-
Surgical correction of pediatric spinal deformities with coexisting intraspinal pathology: A case report and literature review.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Aug 3;12:381. doi: 10.25259/SNI_593_2021. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34513148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CORR Insights®: Is It Possible to Correct Congenital Spinal Deformity Associated With a Tethered Cord Without Prophylactic Intradural Detethering?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Jul;477(7):1698-1699. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000709. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31107328 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is detethering necessary before deformity correction in congenital scoliosis associated with tethered cord syndrome: a meta-analysis of current evidence.Eur Spine J. 2021 Mar;30(3):599-611. doi: 10.1007/s00586-020-06662-7. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Eur Spine J. 2021. PMID: 33201289
-
The complex treatment paradigms for concomitant tethered cord and scoliosis: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Jan 29;7(5):CASE23574. doi: 10.3171/CASE23574. Print 2024 Jan 29. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 38285976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu PS, Elsebaie H, Noordeen MHH. Congenital spinal deformity—a comprehensive assessment at presentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:2255-22559. - PubMed
-
- Hamzaoglu A, Ozturk C, Tezer M, Aydogan M, Sarier M, Talu U. Simultaneous surgical treatment in congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis associated with intraspinal abnormalities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32:2880-2884. - PubMed
-
- Hedequist D, Emans J. Congenital scoliosis: a review and update. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27:106-116. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Yang W, Shen C, Chang M, Li H, Luo Z, Tao H. Surgical treatment of congenital scoliosis associated with tethered cord by thoracic spine-shortening osteotomy without cord detethering. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40:E1103-1109. - PubMed
-
- Kawahara N, Tomita K, Kobayashi T, Abdel-Wanis ME, Murakami H, Akamaru T. Influence of acute shortening on the spinal cord: an experimental study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:613-620. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

