Worsening renal failure in patients with acute heart failure: the importance of cardiac biomarkers
- PMID: 30801997
- PMCID: PMC6437438
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12414
Worsening renal failure in patients with acute heart failure: the importance of cardiac biomarkers
Abstract
Aims: The importance of true worsening renal failure (WRF), which is associated with a poor prognosis, had been suggested in patients with acute heart failure (AHF). The aim of the present study was to establish the biomarker strategy for the prediction of true WRF in AHF.
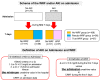
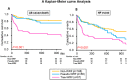
Methods and results: Two hundred eighty-one patients with AHF were analysed. Their biomarkers were measured within 30 min of admission. Patients were assigned to the non-WRF (n = 168), pseudo-WRF (n = 56), or true-WRF (n = 57) groups using the criteria of both acute kidney injury on admission and increasing serum creatinine value during the first 7 days. A Kaplan-Meier curve showed that the survival and heart failure event rate of the true-WRF group within 1000 days was significantly lower than that of the non-WRF and pseudo-WRF groups (P ≤ 0.001). The multivariate Cox regression model also indicated that true WRF was an independent predictor of 1000 day mortality and heart failure events [hazard ratio: 4.315, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.466-7.550, P ≤ 0.001, and hazard ratio: 2.834, 95% CI: 1.893-4.243, P ≤ 0.001, respectively]. The serum heart-type fatty acid-binding protein (s-HFABP) levels were significantly higher in the true-WRF group than in the non-WRF and pseudo-WRF groups (P ≤ 0.001). The multivariate logistic regression model indicated that the predictive biomarker for the true-WRF group was the s-HFABP level (odds ratio: 5.472, 95% CI: 2.729-10.972, P ≤ 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity for indicating the presence of true WRF were 73.7% and 76.8% (area under the curve = 0.831) for s-HFABP in whole patients, respectively, and 94.7% and 72.7% (area under the curve = 0.904) in non-chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, respectively.
Conclusions: Cardiac biomarkers, especially the s-HFABP, might predict the development of true WRF in AHF patients. Furthermore, the predictive value was higher in AHF patients without CKD than in those with CKD.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein; Liver fatty acid-binding protein; Mortality; Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin.
© 2019 The Authors ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in association with the present study.
Figures


References
-
- Cowie MR, Komajda M, Murray‐Thomas T, Underwood J, Ticho B, Investigators P . Prevalence and impact of worsening renal function in patients hospitalized with decompensated heart failure: results of the prospective outcomes study in heart failure (POSH). Eur Heart J 2006; 27: 1216–1222. - PubMed
-
- Kociol RD, Greiner MA, Hammill BG, Phatak H, Fonarow GC, Curtis LH, Hernandez AF. Long‐term outcomes of Medicare beneficiaries with worsening renal function during hospitalization for heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2010; 105: 1786–1793. - PubMed
-
- Hata N, Yokoyama S, Shinada T, Kobayashi N, Shirakabe A, Tomita K, Kitamura M, Kurihara O, Takahashi Y. Acute kidney injury and outcomes in acute decompensated heart failure: evaluation of the RIFLE criteria in an acutely ill heart failure population. Eur J Heart Fail 2010; 12: 32–37. - PubMed
-
- Forman DE, Butler J, Wang Y, Abraham WT, O'Connor CM, Gottlieb SS, Loh E, Massie BM, Rich MW, Stevenson LW, Young JB, Krumholz HM. Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 43: 61–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
