A Comprehensive Model of Factors Associated With Capability to "Live Well" for Family Caregivers of People Living With Mild-to-Moderate Dementia: Findings From the IDEAL Study
- PMID: 30802226
- PMCID: PMC6416095
- DOI: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000285
A Comprehensive Model of Factors Associated With Capability to "Live Well" for Family Caregivers of People Living With Mild-to-Moderate Dementia: Findings From the IDEAL Study
Abstract
Introduction: Understanding key influences on outcomes for caregivers of people with dementia is hampered by inconsistent conceptualization and measurement of outcomes and limited evidence about the relative impact of different variables. We aimed to address these issues.
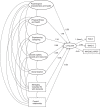
Methods: We analyzed data from 1283 caregivers of community-dwelling individuals with mild-to-moderate dementia in the Improving the experience of Dementia and Enhancing Active Life cohort study. We generated a "living well" latent factor from measures of quality of life, satisfaction with life, and well-being. We used structural equation modelling to derive latent variables for 7 domains reflecting caregivers' perceptions of their personal resources and experiences, and to examine the associations with caregivers' perceptions of their capability to "live well."
Results: The domain of psychological characteristics and psychological health was most strongly related to living well [2.53; 95% confidence interval (CI), 2.08-2.97], followed by physical fitness and physical health (1.48; 95% CI, 1.04-1.91) and experiencing caregiving (1.34; 95% CI, 0.99-1.70). Social capitals, assets and resources (0.68; 95% CI, 0.35-1.00) and relationship with the person with dementia (-0.22; 95% CI, -0.41 to -0.03) had smaller, significant associations. Social location (0.28; 95% CI, -0.33 to 0.89) and managing everyday life with dementia (0.06; 95% CI, -0.15 to 0.28) were not significantly associated with living well.
Discussion: These findings demonstrate the importance of supporting caregivers' psychological and physical health and their ability to develop and maintain positive coping strategies, as well as enabling them to maintain vital social capitals, assets and resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wimo A, Prince M.Prince M. The worldwide costs of dementia. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI); 2015.
-
- Prince M, Knapp M, Guerchet M, et al. Dementia UK Overview, 2nd ed London: Alzheimer’s Society; 2014.
-
- Prince MJ, Prina M, Guerchet M. World Alzheimer Report 2013: Journey of Caring: An Analysis of Long-Term Care for Dementia. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International; 2013.
-
- Garzón-Maldonado FJ, Gutiérrez-Bedmar M, García-Casares N, et al. Health-related quality of life in caregivers of patients with Alzheimer disease. Neurología (English Edition). 2017;32:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Koyama A, Matsushita M, Hashimoto M, et al. Mental health among younger and older caregivers of dementia patients. Psychogeriatrics. 2017;17:108–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

