Implementation of a practical and effective pilot intervention against transmission of Taenia solium by pigs in the Banke district of Nepal
- PMID: 30802248
- PMCID: PMC6405169
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006838
Implementation of a practical and effective pilot intervention against transmission of Taenia solium by pigs in the Banke district of Nepal
Abstract
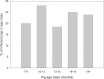
Taenia solium is a zoonotic cestode parasite which causes human neurocysticercosis. Pigs transmit the parasite by acting as the intermediate host. An intervention was implemented to control transmission of T. solium by pigs in Dalit communities of Banke District, Nepal. Every 3 months, pigs were vaccinated with the TSOL18 recombinant vaccine (Cysvax, IIL, India)) and, at the same time, given an oral treatment with 30mg/kg oxfendazole (Paranthic 10% MCI, Morocco). The prevalence of porcine cysticercosis was determined in both an intervention area as well as a similar no intervention control area, among randomly selected, slaughter-age pigs. Post mortem assessments were undertaken both at the start and at the end of the intervention. Participants conducting the post mortem assessments were blinded as to the source of the animals being assessed. At the start of the intervention the prevalence of porcine cysticercosis was 23.6% and 34.5% in the control and intervention areas, respectively. Following the intervention, the prevalence of cysticercosis in pigs from the control area was 16.7% (no significant change), whereas no infection was detected after complete slicing of all muscle tissue and brain in animals from the intervention area (P = 0.004). These findings are discussed in relation to the feasibility and sustainability of T. solium control. The 3-monthly vaccination and drug treatment intervention in pigs used here is suggested as an effective and practical method for reducing T. solium transmission by pigs. The results suggest that applying the intervention over a period of years may ultimately reduce the number of tapeworm carriers and thereby the incidence of NCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control trial of porcine cysticercosis in Uganda using a combination of the TSOL18 vaccination and oxfendazole.Infect Dis Poverty. 2021 Mar 20;10(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00823-6. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021. PMID: 33743828 Free PMC article.
-
A hyperendemic focus of Taenia solium transmission in the Banke District of Nepal.Acta Trop. 2017 Dec;176:78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 28739367 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of protection against porcine cysticercosis by vaccination with recombinant oncosphere antigens.Infect Immun. 2004 Sep;72(9):5292-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5292-5297.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15322025 Free PMC article.
-
Eradication of Taenia solium cysticercosis: a role for vaccination of pigs.Int J Parasitol. 1999 Jun;29(6):811-7. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(99)00051-x. Int J Parasitol. 1999. PMID: 10480718 Review.
-
Vaccination for the prevention of cysticercosis.Dev Biol (Basel). 2004;119:361-8. Dev Biol (Basel). 2004. PMID: 15742647 Review.
Cited by
-
Taenia solium Cysticercosis and Its Impact in Neurological Disease.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020 May 27;33(3):e00085-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00085-19. Print 2020 Jun 17. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32461308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demand for Taenia solium Cysticercosis Vaccine: Lessons and Insights From the Pig Production and Trading Nodes of the Uganda Pig Value Chain.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Apr 27;8:611166. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.611166. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33987216 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate diagnosis of lesions suspected of being caused by Taenia solium in body organs of pigs with naturally acquired porcine cysticercosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jun 25;13(6):e0007408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007408. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31237878 Free PMC article.
-
The Frequency of Porcine Cysticercosis and Factors Associated with Taenia solium Infection in the Municipality of Tuchín-Córdoba, Colombia.Pathogens. 2024 Apr 11;13(4):311. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13040311. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38668266 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Veterinary Vaccines for Livestock as a Strategy to Control Foodborne Parasitic Diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jun 26;10:288. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00288. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32670892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ndimubanzi PC, Carabin H, Budke CM, Nguyen H, Qian YJ, Rainwater E, et al. A systematic review of the frequency of neurocyticercosis with a focus on people with epilepsy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(11):e870 Epub 2010/11/13. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000870 PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2970544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schantz PM, Cruz M, Sarti E, Pawlowski Z. Potential eradicability of taeniasis and cysticercosis. Bull Pan Am Health Organ. 1993;27:397–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

