Conformational analysis of apolipoprotein E3/E4 heteromerization
- PMID: 30802357
- PMCID: PMC6733585
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14794
Conformational analysis of apolipoprotein E3/E4 heteromerization
Abstract
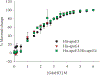
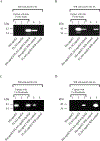
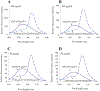
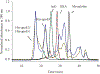
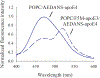
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a 299 residue, exchangeable apolipoprotein that has essential roles in cholesterol homeostasis and reverse cholesterol transport. It is a two-domain protein with the C-terminal (CT) domain mediating protein self-association via helix-helix interactions. In humans, the APOE gene is polymorphic with three common alleles, ε2, ε3, and ε4, occurring in frequencies of ~ 5%, 77%, and 18%, respectively. Heterozygotes expressing apoE3 and apoE4 isoforms, which differ in residue at position 112 in the N-terminal domain (C112 in apoE3 and R112 in apoE4), represent the highest population of ε4 carriers, an allele highly associated with Alzheimer's disease. The objective of this study was to determine if apoE3 and apoE4 have the ability to hybridize to form a heteromer in lipid-free state. Refolding an equimolar mixture of His-apoE3 and FLAG-apoE4 (or vice versa) followed by pull-down and immunoblotting indicated formation of apoE3/apoE4 heteromers. Förster resonance energy transfer between donor fluorophore on one isoform and acceptor on the other, both located in the respective CT domains, revealed a distance of separation of ~ 46 Å between the donor/acceptor pair. Similarly, a quencher placed on one was able to mediate significant quenching of fluorescence emission on the other, indicative of spatial proximity within collisional distance between the two. ApoE3/apoE4 heteromer association was also noted in lipid-associated state in reconstituted lipoprotein particles. The possibility of heteromerization of apoE3/apoE4 bears implications in the potential mitigating role of apoE3 on the folding and physiological behavior of apoE4 and its role in maintaining cholesterol homeostasis.
Keywords: FRET; apolipoprotein E3; apolipoprotein E4; heteromerization; lipoproteins.
© 2019 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
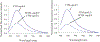
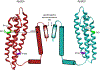
Similar articles
-
Fluorescence study of domain structure and lipid interaction of human apolipoproteins E3 and E4.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1841(12):1716-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.09.019. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25281910 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of the carboxyl-terminal helical segment to the self-association and lipoprotein preferences of human apolipoprotein E3 and E4 isoforms.Biochemistry. 2008 Mar 4;47(9):2968-77. doi: 10.1021/bi701923h. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18201068 Free PMC article.
-
Helical structure, stability, and dynamics in human apolipoprotein E3 and E4 by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 31;114(5):968-973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617523114. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28096372 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E: from cardiovascular disease to neurodegenerative disorders.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Jul;94(7):739-46. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1427-y. Epub 2016 Jun 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27277824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32036033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tau processing and tau-mediated inflammation differ in human APOEε2 and APOEε4 astrocytes.iScience. 2024 Oct 11;27(11):111163. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111163. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39524360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahley RW (2017) Apolipoprotein E: Remarkable Protein Sheds Light on Cardiovascular and Neurological Diseases. Clin. Chem 63, 14–20. - PubMed
-
- Phillips MC (2014) Apolipoprotein E isoforms and lipoprotein metabolism. IUBMB Life 66, 616–623. - PubMed
-
- Mahley RW (1988) Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240, 622–30. - PubMed
-
- Utermann G, Hees M & Steinmetz A (1977) Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature 269, 604–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

