Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context
- PMID: 30802498
- PMCID: PMC6774756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.02.002
Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context
Abstract
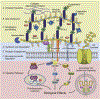
Cell-matrix interactions are fundamental to many developmental, homeostatic, immune and pathologic processes. Hyaluronan (HA), a critical component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) that regulates normal structural integrity and development, also regulates tissue responses during injury, repair, and regeneration. Though simple in its primary structure, HA regulates biological responses in a highly complex manner with balanced contributions from its molecular size and concentration, synthesis versus enzymatic and/or oxidative-nitrative fragmentation, interactions with key HA binding proteins and cell associated receptors, and its cell context-specific signaling. This review highlights the different, but inter-related factors that dictate the biological activity of HA and introduces the overarching themes that weave throughout this special issue of Matrix Biology on hyaluronan.
Keywords: Degradation; Hyaluronan; Receptors; Signaling; Structure; Synthesis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
RCS is a co-founder of Eravon Therapeutics, Inc. that is focused on RHAMM-HA-based therapeutics. RCS also holds the William Buchanan Chair in Pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Neither author have any conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Karamanos NK, Piperigkou Z, Theocharis AD, Watanabe H, Franchi M, Baud S, Brezillon S, Gotte M, Passi A, Vigetti D, Ricard-Blum S, Sanderson RD, Neill T, Iozzo RV, Proteoglycan chemical diversity drives multifunctional cell regulation and therapeutics, Chem. Rev 118 (18) (2018) 9152–9232. - PubMed
-
- Mack M, Inflammation and fibrosis, Matrix Biol. 68–69 (2018) 106–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

