Long-Term Risk of Skin Cancer Among Childhood Cancer Survivors: A DCOG-LATER Cohort Study
- PMID: 30802904
- PMCID: PMC6695299
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djy212
Long-Term Risk of Skin Cancer Among Childhood Cancer Survivors: A DCOG-LATER Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Skin cancer is common after radiotherapy among childhood cancer survivors (CCSs). We studied risks and risk factors for subsequent skin cancers, with emphasis on radiation dose, exposed skin surface area, and chemotherapeutic agents.
Methods: The DCOG-LATER cohort study includes 5-year Dutch CCSs diagnosed 1963-2001. Subsequent skin cancers were identified from record linkages with the Netherlands Cancer Registry and Dutch Pathology Registry. Incidence rates were compared with general population rates. Multivariable Cox regression models were used, applying a novel method of case-control sampling enabling use of tumor location in cohort analyses. All statistical tests were two-sided.
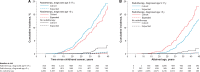
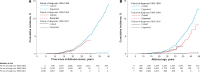
Results: Among 5843 CCSs, 259 developed 1061 basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) (standardized incidence ratio [SIR] = 29.8, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 26.3 to 33.6; excess absolute risk per 10 000 person-years (EAR) = 24.6), 20 had melanoma (SIR = 2.3, 95% CI = 1.4 to 3.5; EAR = 1.1), and 10 had squamous cell carcinoma (SIR = 7.5, 95% CI = 3.6 to 13.8; EAR = 0.8). Cumulative incidence of BCC 40 years after childhood cancer was 19.1% (95% CI = 16.6 to 21.8%) after radiotherapy vs 0.6% expected based on general population rates. After a first BCC, 46.7% had more BCCs later. BCC risk was associated with any radiotherapy to the skin compartment of interest (hazard ratio [HR] = 14.32, 95% CI = 10.10 to 20.29) and with estimated percentage in-field skin surface area (26-75%: HR = 1.99, 95% CI = 1.24 to 3.20; 76-100%: HR = 2.16, 95% CI = 1.33 to 3.53, vs 1-25% exposed; Ptrend among exposed = .002), but not with prescribed radiation dose and likelihood of sun-exposed skin-area. Of all chemotherapy groups examined, only vinca alkaloids increased BCC risk (HR = 1.54, 95% CI = 1.04 to 2.27).
Conclusion: CCSs have a strongly, 30-fold increased BCC risk. BCC risk appears to increase with increasing skin surface area exposed. This knowledge underscores the need for awareness by survivors and their health care providers.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Olsen JH, Moller T, Anderson H, et al. Lifelong cancer incidence in 47, 697 patients treated for childhood cancer in the Nordic countries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;10111:806–813. - PubMed
-
- Reulen RC, Frobisher C, Winter DL, et al. Long-term risks of subsequent primary neoplasms among survivors of childhood cancer. JAMA. 2011;30522:2311–2319. - PubMed
-
- Teepen JC, van Leeuwen FE, Tissing WJ, et al. Long-term risk of subsequent malignant neoplasms after treatment of childhood cancer in the DCOG LATER Study Cohort: role of chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;3520:2288–2298. - PubMed
-
- Daniels LA, Krol AD, Schaapveld M, et al. Long-term risk of secondary skin cancers after radiation therapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Radiother Oncol. 2013;1091:140–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

