The Expression of Leptin and Its Receptor During Tumorigenesis of Diffuse Gliomas such as Astrocytoma and Oligodendroglioma- Grade II, III and IV (NOS)
- PMID: 30803210
- PMCID: PMC6897042
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.2.479
The Expression of Leptin and Its Receptor During Tumorigenesis of Diffuse Gliomas such as Astrocytoma and Oligodendroglioma- Grade II, III and IV (NOS)
Abstract
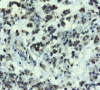
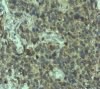
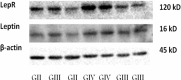
Background: Leptin, an adipocytokine functions via the leptin receptor, OB-Rb that contains an intact intracellular domain and activates the JAK/STAT signalling cascade. It stimulates growth, migration and invasion of cancer cells in vitro potentiating angiogenesis. Recently, the involvement of leptin in tumor progression is being explored. Gliomas exhibit poor prognosis, low survival rates demanding for novel therapeutic regimens resulting in discovery of many potential biomarkers and pharmaceutical targets. We analysed the potential role of leptin and OB-Rb in carcinogenesis of malignant gliomas. Methods: Sixty fresh tissue samples of diffuse gliomas were collected after tumor excision. Real time PCR, immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis and western blot analysis were carried out to assess the expression of leptin and its receptor. Results: The present study demonstrates the expression of leptin and LepR and their involvement in tumor progression. Of the 60 cases, 57 cases (95%) and 53 cases (88.3%) showed amplification for leptin and OB-Rb respectively. The expression of these proteins were measured semi-quantitatively and correlated with degree of malignancy (p<0.05). The bands were visualised on western blot. Conclusion: Leptin may be valued as a pharmaceutical target and anti-leptin compounds could be developed as drugs in mono- or combined therapies for these tumors.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; brain tumors; Real-time PCR.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Higher YAP1 Levels Are Associated With Shorter Survival of Patients With Low Grade Astrocytoma.Anticancer Res. 2024 Jul;44(7):3005-3011. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17113. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38925840
-
Enrichment of branched chain amino acid transaminase 1 correlates with multiple biological processes and contributes to poor survival of IDH1 wild-type gliomas.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jan 20;13(3):3645-3660. doi: 10.18632/aging.202328. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33493139 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in 97 patients with glioma.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 Jul;47(3):442-7. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9681-5. Epub 2011 Nov 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22113362
-
Diffuse Infiltrating Oligodendroglioma and Astrocytoma.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul 20;35(21):2394-2401. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.6737. Epub 2017 Jun 22. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28640702 Review.
-
[Analysis of S100beta-v-erbB transgenic rats prone to brain tumors].Brain Nerve. 2009 Jul;61(7):765-72. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19618853 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Modulation of Adipokines, Adipomyokines, and Sleep Disorders on Carcinogenesis.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 2;12(7):2655. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072655. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diagnostic and Therapeutic Role of Leptin and Its Receptor ObR in Glioblastoma Multiforme.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;12(12):3691. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123691. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33316976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attoub S, Noe V, Pirola L, et al. Leptin promotes invasiveness of kidney and colonic epithelial cells via phosphoinositide 3-kinase, rho, and rac-dependent signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2000;14:2329–38. - PubMed
-
- Beales IL, Garcia-Morales C, Ogunwobi OO, Mutungi G. Adiponectin inhibits leptin-induced oncogenic signaling in oesophageal cancer cells by activation of PTP1B. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;382:150–8. - PubMed
-
- Cheng SP, Yin PH, Hsu YC, et al. Leptin enhances migration of human papillary thyroid cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:1265–71. - PubMed
-
- Frankenberry KA, Somasundar P, McFadden DW, Vona-Davis LC. Leptin induces cell migration and the expression of growth factors in human prostate cancer cells. Am J Surg. 2004;188:560–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

