Nerve injury elevates functional Cav3.2 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn
- PMID: 30803310
- PMCID: PMC6458665
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806919836569
Nerve injury elevates functional Cav3.2 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn
Abstract
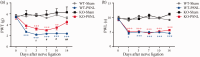
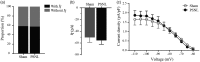
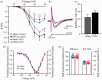
Cav3 channels play an important role in modulating chronic pain. However, less is known about the functional changes of Cav3 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn in neuropathic pain states. Here, we examined the effect of partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL) on either expression or electrophysiological properties of Cav3 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn. Our in vivo studies showed that the blockers of Cav3 channels robustly alleviated PSNL-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, which lasted at least 14 days following PSNL. Meanwhile, PSNL triggered an increase in both mRNA and protein levels of Cav3.2 but not Cav3.1 or Cav3.3 in rats. However, in Cav3.2 knockout mice, PSNL predominantly attenuated mechanical allodynia but not thermal hyperalgesia. In addition, the results of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings showed that both the overall proportion of Cav3 current-expressing neurons and the Cav3 current density in individual neurons were elevated in spinal lamina II neurons from PSNL rats, which could not be recapitulated in Cav3.2 knockout mice. Altogether, our findings reveal that the elevated functional Cav3.2 channels in superficial spinal dorsal horn may contribute to the mechanical allodynia in PSNL-induced neuropathic pain model.
Keywords: Cav3 channels; lamina II neuron; neuropathic pain; spinal dorsal horn; whole-cell patch-clamp recording.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Upregulation of interleukin-6 on Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to neuropathic pain in rats with spinal nerve ligation.Exp Neurol. 2019 Jul;317:226-243. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30872136
-
Enhanced T-type calcium channel 3.2 activity in sensory neurons contributes to neuropathic-like pain of monosodium iodoacetate-induced knee osteoarthritis.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920963807. doi: 10.1177/1744806920963807. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 33054557 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of the spinal dorsal horn clock gene Per1 expression leads to mechanical hypersensitivity via c-jun N-terminal kinase and CCL2 production in mice.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2016 Apr;72:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26808220
-
Targeting T-type/CaV3.2 channels for chronic pain.Transl Res. 2021 Aug;234:20-30. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33422652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scaffold Hopping Affords a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo T-Type Calcium Inhibitor Probe Free From IP Issues.2011 Mar 31 [updated 2013 Mar 22]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2011 Mar 31 [updated 2013 Mar 22]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23762962 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Loganin Ameliorates Painful Diabetic Neuropathy by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Insulin Sensitivity in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide-Induced Diabetic Rats.Cells. 2021 Oct 8;10(10):2688. doi: 10.3390/cells10102688. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685668 Free PMC article.
-
The T-type calcium channel antagonist, Z944, reduces spinal excitability and pain hypersensitivity.Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Sep;178(17):3517-3532. doi: 10.1111/bph.15498. Epub 2021 May 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33871884 Free PMC article.
-
The T-Type Calcium Channel Cav3.2 in Somatostatin Interneurons in Spinal Dorsal Horn Participates in Mechanosensation and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 8;16:875726. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.875726. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35465611 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanisms of Plasticity of Nociceptive Ion Channels in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 28;3:869735. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2022.869735. eCollection 2022. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35419564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalamocortical Circuit Controls Neuropathic Pain via Up-regulation of HCN2 in the Ventral Posterolateral Thalamus.Neurosci Bull. 2023 May;39(5):774-792. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00989-5. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 36538279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuner R, Flor H. Structural plasticity and reorganisation in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017; 18: 20–30. - PubMed
-
- Woolf CJ, Salter MW. Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science 2000; 288: 1765–1769. - PubMed
-
- Benarroch EE. Ion channels in nociceptors: recent developments. Neurology 2015; 84: 1153–1164. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP, Striessnig J. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 2005; 57: 411–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

