Precision microcatheter shaping in vertebrobasilar aneurysm coiling
- PMID: 30803335
- PMCID: PMC6607607
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019918824012
Precision microcatheter shaping in vertebrobasilar aneurysm coiling
Abstract
Background: Inventing an optimal curve on a microcatheter is required for successful intracranial aneurysm coiling. Shaping microcatheters for vertebrobasilar artery aneurysm coiling is difficult because of the vessel's long, tortuous and mobile anatomy. To overcome this problem, we devised a new method of shaping the microcatheter by using the patient's specific vessel anatomy and the highly shapable microcatheter. We report our preliminary results of treating posterior circulation aneurysms by this method.
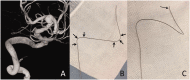
Methods: An unshaped microcatheter (Excelsior XT-17; Stryker Neurovascular, Fremont, CA, USA) was pretreated by exposure to the patient's vessel for five minutes. The microcatheter was placed in the vicinity of the targeted aneurysm and was left in contact with the patient's vessel before extraction. This treatment precisely formed a curve on the microcatheter shaft identical to the patient's vessel anatomy. Following the pretreatment, the tip of the microcatheter was steam shaped according to the long axis of the target aneurysm. Five consecutive vertebrobasilar aneurysms were treated using this shaping method and evaluated for the clinical and anatomical outcomes and microcatheter accuracy and stability.
Results: All of the designed microcatheters matched the vessel and aneurysm anatomy except in one case that required a single modification. All aneurysms were successfully catheterized without the assistance of a microguidewire, and matched the long axis of the aneurysm. All microcatheters retained stability until the end of the procedure.
Conclusions: A precise microcatheter shaping for a vertebrobasilar artery aneurysm may be achieved by using the patient's actual vessel anatomy and the highly shapable microcatheter.
Keywords: Microcatheter shaping; coiling; intracranial aneurysm.
Figures


References
-
- Kwon BJ, Im SO, Park JC, et al. Shaping and navigating methods of microcatheters for endovascular treatment of paraclinoid aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2010; 67: 34–40. - PubMed
-
- Hwang JH, Rho HG, Chun YI, et al. Endovascular coil embolization of very small intracranial aneurysms. Neuroradiology 2011; 53: 349–357. - PubMed
-
- Namba K, Higaki A, Kaneko N, et al. Microcatheter shaping for intracranial aneurysm coiling using the 3-dimensional printing rapid prototyping technology: preliminary result in the first 10 consecutive cases. World Neurosurg 2015; 84: 178–186. - PubMed
-
- Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, et al. Endovascular treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms by electrothrombosis using electrically detachable coils. J Neurosurg 1992; 77: 515–524. - PubMed
-
- Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years’ experience. J Neurosurg 2003; 98: 959–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

