A Noninvasive Method to Reduce Radiotherapy Positioning Error Caused by Respiration for Patients With Abdominal or Pelvic Cancers
- PMID: 30803363
- PMCID: PMC6378633
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033819825865
A Noninvasive Method to Reduce Radiotherapy Positioning Error Caused by Respiration for Patients With Abdominal or Pelvic Cancers
Abstract
Purpose: To develop an infrared optical method of reducing surface-based registration error caused by respiration to improve radiotherapy setup accuracy for patients with abdominal or pelvic tumors.
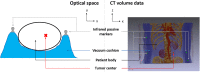
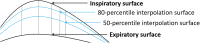
Materials and methods: Fifteen patients with abdominal or pelvic tumors who received radiation therapy were prospectively included in our study. All patients were immobilized with vacuum cushion and underwent cone-beam computed tomography to validate positioning error before treatment. For each patient, after his or her setup based on markers fixed on immobilization device, initial positioning errors in patient left-right, anterior-posterior, and superior-inferior directions were validated by cone-beam computed tomography. Then, our method calculated mismatch between patient and immobilization device based on surface registration by interpolating between expiratory- and inspiratory-phase surface to find the specific phase to best match the surface in planning computed tomography scans. After adjusting the position of treatment couch by the shift proposed by our method, a second cone-beam computed tomography was performed to determine the final positioning error. A comparison between initial and final setup error will be made to validate the effectiveness of our method.
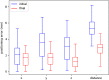
Results: Final positioning error confirmed by cone-beam computed tomography is 1.59 (1.82), 1.61 (1.84), and 1.31 (1.38) mm, reducing initial setup error by 24.52%, 51.04%, and 53.63% in patient left-right, anterior-posterior, and superior-inferior directions, respectively. Wilcoxon test showed that our method significantly reduced the 3-dimensional distance of positioning error ( P < .001).
Conclusion: Our method can significantly improve the setup precision for patients with abdominal or pelvic tumors in a noninvasive way by reducing the surface-based registration error caused by respiration.
Keywords: patient setup; radiation therapy; respiratory-phase interpolation; respiratory-phase match; surface-based registration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
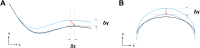
Similar articles
-
[Comparison of setup errors between two immobilization methods in prostate cancer radiotherapy based on cone-beam computed tomography].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Aug 18;57(4):692-697. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.010. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40754905 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Impact of immobilization on intrafraction motion for spine stereotactic body radiotherapy using cone beam computed tomography.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Oct 1;84(2):520-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.039. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22401920
-
A Noninvasive Body Setup Method for Radiotherapy by Using a Multimodal Image Fusion Technique.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Dec;16(6):1187-1193. doi: 10.1177/1533034617740302. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 29333959 Free PMC article.
-
A review of setup error in supine breast radiotherapy using cone-beam computed tomography.Med Dosim. 2016 Autumn;41(3):225-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Med Dosim. 2016. PMID: 27311516 Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Clinical Implementation of Pelvic Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Only Planning for External Beam Radiation Therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Nov 1;105(3):479-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.2530. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31271829
References
-
- Kavanagh BD, Miften M, Rabinovitch RA. Advances in treatment techniques: stereotactic body radiation therapy and the spread of hypofractionation. Cancer J. 2011;17(3):177–181. - PubMed
-
- Baumann M, Krause M, Overgaard J, et al. Radiation oncology in the era of precision medicine. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(4):234–249. - PubMed
-
- Chen MF, Tseng CJ, Tseng CC, Kuo YC, Yu CY, Chen WC. Clinical outcome in posthysterectomy cervical cancer patients treated with concurrent cisplatin and intensity-modulated pelvic radiotherapy: comparison with conventional radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67(5):1438–1444. - PubMed
-
- Fenoglietto P, Laliberte B, Allaw A, et al. Persistently better treatment planning results of intensity-modulated (IMRT) over conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) in prostate cancer patients with significant variation of clinical target volume and/or organs-at-risk. Radiother Oncol. 2008;88(1):77–87. - PubMed
-
- Hadziahmetovic M, Loo BW, Timmerman RD, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (stereotactic ablative radiotherapy) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer-updates of radiobiology, techniques, and clinical outcomes. Discov Med. 2010;9(48):411–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

