How to eliminate taeniasis/cysticercosis: porcine vaccination and human chemotherapy (Part 2)
- PMID: 30803437
- PMCID: PMC6390339
- DOI: 10.1186/s12976-019-0100-x
How to eliminate taeniasis/cysticercosis: porcine vaccination and human chemotherapy (Part 2)
Abstract
Background: The application of effective vaccines against pig cysticercosis and mass chemotherapy against pig cysticercosis and human taeniasis have shown the feasibility of interrupting the parasite's life cycle in endemic areas.
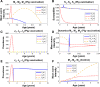
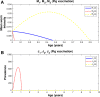
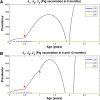
Methods: A mathematical model that divides the population into susceptible, infected, and vaccinated individuals is formulated. The model is based upon the life cycle of the parasite. Computer numerical simulation experiments to evaluate the impact of pig vaccination under different vaccination schedules, and combined intervention strategies including pig vaccination and anthelmintic treatment against human taeniasis are carried out.
Results: Vaccination against either pig cysticercosis or against human taeniasis will influence the transmission dynamics not only among vaccinees but also the dynamics of the other hosts as well. When the protective efficacy and/or the coverage rate is less than 100%, different mass interventions like vaccinating the pig population twice in combination with chemotherapeutic treatment against human taeniasis, the elimination of the infection in both pigs and humans can also be achieved.
Conclusions: Our mathematical model has the potential for planning, and designing effective intervention strategies including both mass vaccination and/or chemotherapeutic treatment to eliminate pig cysticercosis, human taeniasis and human neurocysticercosis. The model can be adapted to any given community with mild, moderate endemicity, or even in hyperendemic regions.
Keywords: Chemotherapeutic interventions; Computer simulation experiments; Elimination; Eradication; Public health; Susceptible-infected mathematical model; Taenia-cysticercosis; Vaccination strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
NYS is a PhD student of Biomedical Sciences in the Theoretical Biology Group. JRB is Academic Technician of the Theoretical Biology Group; MVJ is Full Professor and Head of the Theoretical Biology Group; JPL is Full Professor in the Department of Immunology.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This study does not contain any individual person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Grove DI. A History of Human Helminthology. Wallingford: C·A·B International; 1990. p. 848.
-
- World Health Organization. Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2012. https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/en/. Accessed Jan 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

