Neuronal scaffolding protein spinophilin is integral for cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization and ERK1/2 activation
- PMID: 30803445
- PMCID: PMC6388481
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-019-0434-7
Neuronal scaffolding protein spinophilin is integral for cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization and ERK1/2 activation
Abstract
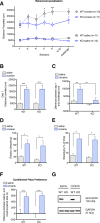
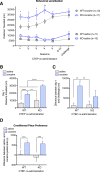
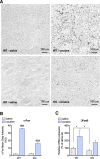
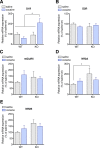
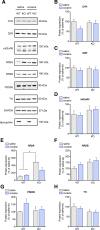
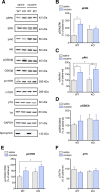
Spinophilin is a scaffolding protein enriched in dendritic spines with integral roles in the regulation of spine density and morphology, and the modulation of synaptic plasticity. The ability of spinophilin to alter synaptic strength appears to involve its scaffolding of key synaptic proteins, including the important structural element F-actin, AMPA/NMDA modulator protein phosphatase 1, and neuromodulatory G-protein coupled receptors, including dopamine receptor D2 and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5. Additionally, spinophilin is highly expressed in the striatum, a brain region that is fundamentally involved in reward-processing and locomotor activity which receives both glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the role of spinophilin in behavioral responses to cocaine, evaluating wild-type and spinophilin knockout mice followed by the examination of underlying molecular alterations. Although acute locomotor response was not affected, deletion of spinophilin blocked the development and expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine while maintaining normal conditioned place preference. This behavioral alteration in spinophilin knockout mice was accompanied by attenuated c-Fos and ∆FosB expression following cocaine administration and blunted cocaine-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the striatum, with no change in other relevant signaling molecules. Therefore, we suggest spinophilin fulfills an essential role in cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization, likely via ERK1/2 phosphorylation and induction of c-Fos and ∆FosB in the striatum, a mechanism that may underlie specific processes in cocaine addiction.
Keywords: Behavioral sensitization; Cocaine; Drug addiction; Spinophilin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were performed following the Canadian Council of Animal Care guidelines and approved by the University of Ottawa animal care committee (protocol no. CMM2519). Human ethics approval is not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles for spinophilin and neurabin in dopamine-mediated plasticity.Neuroscience. 2006 Jul 7;140(3):897-911. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.067. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16600521
-
Involvement of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade for cocaine-rewarding properties.J Neurosci. 2000 Dec 1;20(23):8701-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08701.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11102476 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity-associated gene Krox24/Zif268 is required for long-lasting behavioral effects of cocaine.J Neurosci. 2006 May 3;26(18):4956-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4601-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16672671 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 activation by addictive drugs: a signal toward pathological adaptation.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 15;76(12):917-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24844603 Review.
-
[Advanced findings on the molecular mechanisms for behavioral sensitization to psychostimulants].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Jan;117(1):5-12. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.5. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11233297 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Modulation of dendritic spines by protein phosphatase-1.Adv Pharmacol. 2021;90:117-144. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Adv Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33706930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IQ Motif Containing GTPase Activating Proteins (IQGAPs), A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs) and Kinase Suppressor of Ras Proteins (KSRs) in Scaffolding Oncogenic Pathways and Their Therapeutic Potential.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 6;7(50):45837-45848. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05505. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for incentive salience sensitization as a pathway to alcohol use disorder.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Dec;107:897-926. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.10.009. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 31672617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Trafficking and its Role in Drug-Induced Neurobehavioral Plasticity.Brain Plast. 2021 Oct 19;7(2):61-76. doi: 10.3233/BPL-210120. eCollection 2021. Brain Plast. 2021. PMID: 34868874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinophilin Limits Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Scaffolding to the Postsynaptic Density and Cell Type Specifically Mediates Excessive Grooming.Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Jun 1;93(11):976-988. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36822932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen PB, Zachariou V, Svenningsson P, Lepore AC, Centonze D, Costa C, Rossi S, Bender G, Chen G, Feng J, Synder GL, Bernardi G, Nestler EJ, Yan Z, Calabresi P, Greengard P. Distinct roles for spinophilin and neurabin in dopamine-mediated plasticity. Neuroscience. 2006;140(3):897–911. - PubMed
-
- Areal LB, Herlinger AL, Pelicao FS, Martins-silva C, Pires RGW. Crack cocaine inhalation induces schizophrenia-like symptoms and molecular alterations in mice prefrontal cortex. J Psychiatr Res. 2017;91:57–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

