Screening for periodontal diseases by non-dental health professionals: a protocol for a systematic review and overview of reviews
- PMID: 30803450
- PMCID: PMC6388477
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-019-0977-9
Screening for periodontal diseases by non-dental health professionals: a protocol for a systematic review and overview of reviews
Abstract
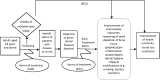
Background: Periodontal diseases are responsible for a vast burden of disease globally and are associated with other severe illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases or diabetes. Tests for early diagnosis of periodontal diseases and effective treatments are available. The effectiveness of screening for periodontal diseases to detect periodontal diseases at an early stage during periodic health examinations at primary care facilities, however, is unclear. The objective of this systematic review is to assess the benefits and risks of screening for periodontal diseases in adults during the periodic health examinations.
Methods: We will use two methodological approaches: (1) a systematic review to assess the effectiveness and risk of harms of screening for periodontal diseases during periodic health examinations and (2) an overview of systematic reviews to determine the effectiveness of treatment approaches for early periodontal disease. We will search electronic databases (Ovid MEDLINE, Embase.com , the Cochrane Library, Epistemonikos, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination databases, PubMed (non-MEDLINE content)) for published studies as well as sources for grey literature to detect unpublished studies. Two authors will independently screen abstracts and full texts using pre-defined eligibility criteria, select studies, extract data, and assess the risk of bias of included studies or reviews. In general, we will conduct a systematic narrative synthesis. Criteria for conducting meta-analyses were defined a priori. Our primary outcomes of interest are tooth loss, loosening of teeth, and depletion of bone tissue. Secondary outcomes are gingivitis/gum inflammation, pocket depths, dental hygiene, lifestyle modifications (e.g., smoking, alcohol, nutrition), and toothache. We consulted a panel of experts and patient representatives to prioritize these outcomes. Two investigators will assess independently the certainty of the evidence for each outcome using the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach.
Discussion: We anticipate that our review will highlight the gaps in the available evidence about the effectiveness of screening for periodontal diseases during periodic health examinations. Implications for screening programs may be based on linked evidence about the validity of available screening tools and the effectiveness of early treatment.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO CRD42017081150.
Keywords: Gingivitis; Periodontal diseases; Periodontitis; Screening; Screening tools; Systematic review; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases