Analysis of Pleiotropic Effects of Nivolumab in Pretreated Advanced or Recurrent Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cases
- PMID: 30804134
- PMCID: PMC6506318
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11503
Analysis of Pleiotropic Effects of Nivolumab in Pretreated Advanced or Recurrent Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cases
Abstract
Background/aim: Nivolumab is an immune checkpoint inhibitor for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We investigated the safety and efficacy of nivolumab by analyzing the response factor, adverse effects (AE), and the post-treatment condition of pretreated advanced or recurrent NSCLC patients.
Patients and methods: Nivolumab (3 mg/kg) was administered to 79 pre-treated NSCLC patients from December 2015 to January 2018. Nivolumab efficacy and AE were assessed using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors and the Common Terminology Criteria, respectively.
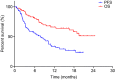
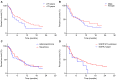
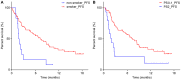
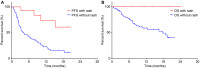
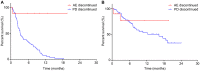
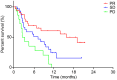
Results: Progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly prolonged in cases where the therapeutic effect of the pretreatment was a partial response (p=0.0004). Five cases (6.3%) experienced grade 3-4 AEs. PFS was significantly prolonged in the skin rash group versus the non-skin rash group, and in patients where nivolumab treatment was discontinued.
Conclusions: Long-term survival was observed in patients with skin rash. Therapeutic effect of nivolumab immediately following its administration appears to be favorable for survival.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; durable response; immune-related adverse event; nivolumab; non-small cell lung cancer; programmed cell death ligand 1.
Copyright© 2019, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare regarding the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Early Death in Japanese Patients With Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Treated With Nivolumab.Clin Lung Cancer. 2018 Mar;19(2):e171-e176. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29133121
-
Nivolumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients who failed prior platinum-based chemotherapy.Lung Cancer. 2018 Aug;122:234-242. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.05.023. Epub 2018 May 24. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30032838 Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab Monotherapy for First-Line Treatment of Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Sep 1;34(25):2980-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.9929. Epub 2016 Jun 27. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27354485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab for the treatment of Japanese patients with advanced metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a review of clinical trial evidence for efficacy and safety.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018 Jan-Dec;12:1753466618801167. doi: 10.1177/1753466618801167. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018. PMID: 30249170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The safety of nivolumab for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Jan;16(1):101-109. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1267725. Epub 2016 Dec 11. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 27910704 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin Infiltrate Composition as a Telling Measure of Responses to Checkpoint Inhibitors.JID Innov. 2023 Feb 9;3(5):100190. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2023.100190. eCollection 2023 Sep. JID Innov. 2023. PMID: 37554516 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous adverse events in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors and their association with survival: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 21;12(1):20038. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24286-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36414662 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence Rates of Cutaneous Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Oncol. 2025 Mar 27;32(4):195. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32040195. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40277752 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends on precision cancer medicine-related rashes (2008-2021): A bibliographic study.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 26;13:1002034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1002034. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki S, Ishida T, Yoshikawa K, Ueda R. Current status of immunotherapy. Japanese J Clin Oncol. 2016;46(3):191–203. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Thudium KB, Han M, Wang XT, Huang H, Feingersh D, Garcia C, Wu Y, Kuhne M, Srinivasan M, Singh S, Wong S, Garner N, Leblanc H, Bunch RT, Blanset D, Selby MJ, Korman AJ. In vitro characterization of the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab, BMS-936558, and in vivo toxicology in non-human primates. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;9:846–856. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman J, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, DeCamp MM, Dilling TJ, Dobelbower M, Doebele RC, Govindan R, Gubens MA, Hennon M, Horn L, Komaki R, Lackner RP, Lanuti M, Leal TA, Leisch LJ, Lilenbaum R, Lin J, Loo BW Jr, Martins R, Otterson GA, Reckamp K, Riely GJ, Schild SE, Shapiro TA, Stevenson J, Swanson SJ, Tauer K, Yang SC, Gregory K, Hughes M. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5 2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017;15(4):504–535. - PubMed
-
- Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crino L, Eberhardt W, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes E, Holgado E, Waterhouse D, Ready N, Gaino J, Fontera OA, Havel L, Steins M, Grassino M, Aerts J, Domine M, Paz-Ares L, Reck M, Baudelet C, Harbison CT, Lestini B, Spigel DR. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;9:123–135. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
