miR-206 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targetting glutaminase
- PMID: 30804229
- PMCID: PMC6900431
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20181108
miR-206 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targetting glutaminase
Abstract
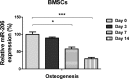
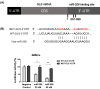
Osteoblast-mediated bone formation is a complex process involving various pathways and regulatory factors, including cytokines, growth factors, and hormones. Investigating the regulatory mechanisms behind osteoblast differentiation is important for bone regeneration therapy. miRNAs are known as important regulators, not only in a variety of cellular processes, but also in the pathogenesis of bone diseases. In the present study, we investigated the potential roles of miR-206 during osteoblast differentiation. We report that miR-206 expression was significantly down-regulated in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) at days 7 and 14 during osteogenic induction. Furthermore, miR-206 overexpressing BMSCs showed attenuated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, Alizarin Red staining, and osteocalcin secretion. The mRNA levels of osteogenic markers, Runx2 and Osteopontin (OPN), were significantly down-regulated in miR-206 overexpressing BMSCs. We observed that significantly increased glutamine uptake at days 7 and 14 during the osteogenic induction and inhibition of glutamine metabolism by knocking down glutaminase (GLS)-suppressed osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Here, we discover that miR-206 could directly bind to the 3'-UTR region of GLS mRNA, resulting in suppressed GLS expression and glutamine metabolism. Finally, restoration of GLS in miR-206 overexpressing BMSCs led to recovery of glutamine metabolism and osteogenic differentiation. In summary, these results reveal a new insight into the mechanisms of the miR-206-mediated osteogenesis through regulating glutamine metabolism. Our study may contribute to the development of therapeutic agents against bone diseases.
Keywords: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; glutaminase (GLS); microRNA-206; osteogenic differentiation.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Park J., Wada S., Ushida T. and Akimoto T. (2015) The microRNA-23a has limited roles in bone formation and homeostasis in vivo. Physiol. Res. 64, 711–719 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

