Potential therapeutic molecular targets for blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 30804237
- PMCID: PMC6425837
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.251190
Potential therapeutic molecular targets for blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
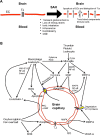
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage remains serious hemorrhagic stroke with high morbidities and mortalities. Aneurysm rupture causes arterial bleeding-induced mechanical brain tissue injuries and elevated intracranial pressure, followed by global cerebral ischemia. Post-subarachnoid hemorrhage ischemia, tissue injuries as well as extravasated blood components and the breakdown products activate microglia, astrocytes and Toll-like receptor 4, and disrupt blood-brain barrier associated with the induction of many inflammatory and other cascades. Once blood-brain barrier is disrupted, brain tissues are directly exposed to harmful blood contents and immune cells, which aggravate brain injuries furthermore. Blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage may be developed by a variety of mechanisms including endothelial cell apoptosis and disruption of tight junction proteins. Many molecules and pathways have been reported to disrupt the blood-brain barrier after subarachnoid hemorrhage, but the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Multiple independent and/or interconnected signaling pathways may be involved in blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage. This review provides recent understandings of the mechanisms and the potential therapeutic targets of blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Keywords: TLR4; Toll-like receptor 4; blood-brain barrier; early brain injury; endothelial cell; inflammation; matricellular protein; subarachnoid hemorrhage; tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Chen G, Zhang S, Shi J, Ai J, Hang C. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) on JAK2/STAT3 pathway and endothelial apoptosis in the rabbit basilar artery after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cytokine. 2009;45:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Connolly ES, Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Kirkness CJ, Naidech AM, Ogilvy CS, Patel AB, Thompson BG, Vespa P American Heart Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Clinical Cardiology. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012;43:1711–1737. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

