CXCR7 promotes melanoma tumorigenesis via Src kinase signaling
- PMID: 30804329
- PMCID: PMC6389959
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1442-3
CXCR7 promotes melanoma tumorigenesis via Src kinase signaling
Abstract
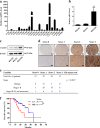
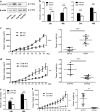
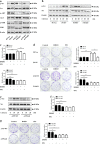
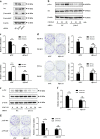
Chemokine receptors have been documented to exert critical functions in melanoma progression. However, current drugs targeting these receptors have limited efficacy in clinical applications, suggesting the urgency to further explore the roles of chemokine receptors in melanoma. Here we found that C-X-C chemokine receptor 7 (CXCR7) was the most highly expressed chemokine receptor in murine melanoma cell lines. In addition, the expression level of CXCR7 was positively correlated with melanoma progression in the clinical samples. High CXCR7 expression was associated with shorter overall survival in melanoma patients. Increased expression of CXCR7 augmented melanoma proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo, whereas knockout of CXCR7 exhibited significant inhibitory effects. Moreover, our data elucidated that CXCR7 activated Src kinase phosphorylation in a β-arrestin2-dependent manner. The administration of the Src kinase inhibitor PP1 or siRNA specific for β-arrestin2 abolished CXCR7-promoted cell proliferation. Importantly, CXCR7 also regulated melanoma angiogenesis and the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Subsequent investigations revealed a novel event that the activation of the CXCR7-Src axis stimulated the phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) to accelerate the translation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), which enhanced the secretion of VEGF from melanoma cells. Collectively, our results illuminate the crucial roles of CXCR7 in melanoma tumorigenesis, and indicate the potential of targeting CXCR7 as new therapeutic strategies for melanoma treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The chemokine receptor CXCR7 is a critical regulator for the tumorigenesis and development of papillary thyroid carcinoma by inducing angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.Tumour Biol. 2016 Feb;37(2):2415-23. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4051-5. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26383519
-
The critical role of mast cell-derived hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human and mice melanoma growth.Int J Cancer. 2013 Jun 1;132(11):2492-501. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27937. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23161568
-
Chemokine receptor 7 targets the vascular endothelial growth factor via the AKT/ERK pathway to regulate angiogenesis in colon cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(11):5327-5340. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2426. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31348616 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR7 in tumorigenesis and progression.Chin J Cancer. 2010 Apr;29(4):456-9. doi: 10.5732/cjc.009.10404. Chin J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20346226 Review.
-
The Critical Role and Therapeutic Potential of the CXCR Family in Skin Diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Apr 29;30(5):26759. doi: 10.31083/FBL26759. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40464497 Review.
Cited by
-
The expression and significance of mTORC1 in diabetic retinopathy.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul 20;20(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01553-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32689970 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine promotes the malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the MOR/Src/mTOR pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Nov 25;21(1):622. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02334-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34823532 Free PMC article.
-
CXC Chemokine Receptors in the Tumor Microenvironment and an Update of Antagonist Development.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;178:1-40. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_35. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32816229 Review.
-
Chondroitin polymerizing factor (CHPF) promotes development of malignant melanoma through regulation of CDK1.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 1;11(7):496. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2526-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32612115 Free PMC article.
-
Germinal Center-Related G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Antibody-Mediated Autoimmune Skin Diseases: from Basic Research to Clinical Trials.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022 Dec;63(3):357-370. doi: 10.1007/s12016-022-08936-y. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35674978 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

