Apical-basal polarity inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour metastasis by PAR-complex-mediated SNAI1 degradation
- PMID: 30804505
- PMCID: PMC6546105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-019-0291-8
Apical-basal polarity inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour metastasis by PAR-complex-mediated SNAI1 degradation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Apical-basal polarity inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour metastasis by PAR-complex-mediated SNAI1 degradation.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Sep;25(9):1385. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01223-8. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37580389 No abstract available.
Abstract
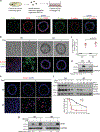
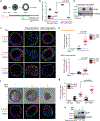
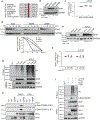
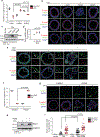
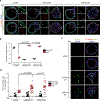
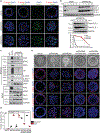
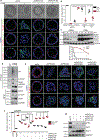
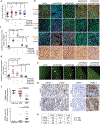
Loss of apical-basal polarity and activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) both contribute to carcinoma progression and metastasis. Here, we report that apical-basal polarity inhibits EMT to suppress metastatic dissemination. Using mouse and human epithelial three-dimensional organoid cultures, we show that the PAR-atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) polarity complex inhibits EMT and invasion by promoting degradation of the SNAIL family protein SNAI1. Under intact apical-basal polarity, aPKC kinases phosphorylate S249 of SNAI1, which leads to protein degradation. Loss of apical-basal polarity prevents aPKC-mediated SNAI1 phosphorylation and stabilizes the SNAI1 protein to promote EMT and invasion. In human breast tumour xenografts, inhibition of the PAR-complex-mediated SNAI1 degradation mechanism promotes tumour invasion and metastasis. Analyses of human breast tissue samples reveal negative correlations between PAR3 and SNAI1 protein levels. Our results demonstrate that apical-basal polarity functions as a critical checkpoint of EMT to precisely control epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity during tumour metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no financial and non-financial competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Epithelial polarity limits EMT.Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Mar;21(3):299-300. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0284-7. Nat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30824839 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zen K et al. Defective expression of polarity protein PAR-3 gene (PARD3) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 28, 2910–2918 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Assemat E, Bazellieres E, Pallesi-Pocachard E, Le Bivic A & Massey-Harroche D Polarity complex proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778, 614–630 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Lee M & Vasioukhin V Cell polarity and cancer--cell and tissue polarity as a non-canonical tumor suppressor. J Cell Sci 121, 1141–1150 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

