Anti-inflammatory drug-eluting implant model system to prevent wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis
- PMID: 30804671
- PMCID: PMC6371946
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S188193
Anti-inflammatory drug-eluting implant model system to prevent wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis
Abstract
Background: Aseptic loosening, as a consequence of an extended inflammatory reaction induced by wear particles, has been classified as one of the most common complications of total joint replacement (TJR). Despite its high incidence, no therapeutical approach has yet been found to prevent aseptic loosening, leaving revision as only effective treatment. The local delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs to modulate wear-induced inflammation has been regarded as a potential therapeutical approach to prevent aseptic-loosening.
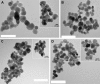
Methods: In this context, we developed and characterized anti-inflammatory drug-eluting TiO2 surfaces, using nanoparticles as a model for larger surfaces. The eluting surfaces were obtained by conjugating dexamethasone to carboxyl-functionalized TiO2 particles, obtained by using either silane agents with amino or mercapto moieties.
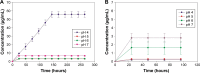
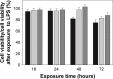
Results: Zeta potential measurements, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and drug release results suggest that dexamethasone was successfully loaded onto the TiO2 particles. Release was pH dependent and greater amounts of drug were observed from amino route functionalized surfaces. The model-system was then tested for its cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory properties in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Dexamethasone released from amino route functionalized surfaces TiO2 particles was able to decrease LPS-induced nitric oxide (NO) and TNF-a production similarly to pure DEX at the same concentration; DEX released from mercapto route functionalized surfaces was at a too low concentration to be effective.
Conclusion: Dexamethasone released from amino functionalized titanium can offer the possibility of preventing asepting loosening of joint replacement devices.
Keywords: TJR; aseptic loosening; dexamethasone; implant; macrophages; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA interference targeting TNF-alpha in macrophages inhibits particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis in vitro and in vivo.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Oct 18;17(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1290-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27756280 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular prodrug of dexamethasone prevents particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis with reduced systemic side effects.J Control Release. 2014 Feb 10;175:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.11.024. Epub 2013 Dec 8. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24326124 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-induced osteolysis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.09.031. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27728897
-
Periprosthetic osteolysis: genetics, mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.Can J Surg. 2012 Dec;55(6):408-17. doi: 10.1503/cjs.003711. Can J Surg. 2012. PMID: 22992398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress on the relationship between wear debris-induced apoptosis and aseptic loosening of prosthesis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013 Sep;26(9):791-6. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013. PMID: 24416919 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Propionate and butyrate attenuate macrophage pyroptosis and osteoclastogenesis induced by CoCrMo alloy particles.Mil Med Res. 2022 Aug 23;9(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00404-0. Mil Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35996168 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Autophagy in the Fibroblasts by Titanium Particles Increased the Release of CX3CL1 and Promoted the Chemotactic Migration of Monocytes.Inflammation. 2020 Apr;43(2):673-685. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01149-0. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 31845051
-
Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants and impact on cells.Int J Implant Dent. 2020 Sep 12;6(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40729-020-00247-1. Int J Implant Dent. 2020. PMID: 32918144 Free PMC article.
-
Amplify antimicrobial photo dynamic therapy efficacy with poly-beta-amino esters (PBAEs).Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86773-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790379 Free PMC article.
-
PMMA bone cement containing long releasing silica-based chlorhexidine nanocarriers.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 29;16(9):e0257947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257947. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34587194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Manen MD, Nace J, Mont MA. Management of primary knee osteoarthritis and indications for total knee arthroplasty for general practitioners. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112(11):709–715. - PubMed
-
- Takakubo Y, Berce A, Trebše R. Wear and corrosion in the loosening of total joint replacements (TJRs) In: Yan Y, editor. Bio-Tribocorrosion in Biomaterials and Medical Implants. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing; 2013. pp. 74–110.
-
- Kallala RF, Vanhegan IS, Ibrahim MS, Sarmah S, Haddad FS. Financial analysis of revision knee surgery based on NHS Tariffs and hospital costs: does it pay to provide a revision service? Bone Joint J. 2015;2:197–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

