The Link Between Tau and Insulin Signaling: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease and Other Tauopathies
- PMID: 30804755
- PMCID: PMC6371747
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00017
The Link Between Tau and Insulin Signaling: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease and Other Tauopathies
Abstract
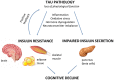
The microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) is mainly identified as a tubulin binding protein essential for microtubule dynamics and assembly and for neurite outgrowth. However, several other possible functions for Tau remains to be investigated. Insulin signaling is important for synaptic plasticity and memory formation and therefore is essential for proper brain function. Tau has recently been characterized as an important regulator of insulin signaling, with evidence linking Tau to brain and peripheral insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction. In line with this notion, the hypothesis of Tau pathology as a key trigger of impaired insulin sensitivity and secretion has emerged. Conversely, insulin resistance can also favor Tau dysfunction, resulting in a vicious cycle of these events. In this review article, we discuss recent evidence linking Tau pathology, insulin resistance and insulin deficiency. We further highlight the deleterious consequences of Tau pathology-induced insulin resistance to the brain and/or peripheral tissues, suggesting that these are key events mediating cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other tauopathies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; MAPT; cognitive decline; diabetes; insulin resistance; tau protein; tauopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Angelini A., Bendini C., Neviani F., Bergamini L., Manni B., Trenti T., et al. (2009). Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1): relation with cognitive functioning and neuroimaging marker of brain damage in a sample of hypertensive elderly subjects. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 49, 5–12. 10.1016/j.archger.2009.09.006 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

