The Role of Motivational Regulation in Exam Preparation: Results From a Standardized Diary Study
- PMID: 30804828
- PMCID: PMC6370677
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00081
The Role of Motivational Regulation in Exam Preparation: Results From a Standardized Diary Study
Abstract
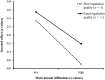
Previous studies have shown that the use of motivational regulation strategies has the potential to sustain invested effort and persistence in the learning process. Combining different methods (questionnaires and standardized diaries), the present study aimed to determine the role of motivational regulation in an exam preparation period. Motivational regulation is differentiated in a quantitative (extent of strategy use) and a qualitative (planning, implementing, monitoring, and correcting strategy use) aspect. One hundred and fifteen university students reported the quantity and quality of their motivational regulation strategy use in a pretest and kept a standardized learning diary focused on motivational difficulties and invested effort over a 14-day period just before an exam in their studies. Exam performance was assessed afterward. Results revealed positive effects of both aspects of motivational regulation on invested effort in exam preparation and exam performance. Moreover, a high quality of motivational regulation was associated with reduced negative effects of motivational difficulties on invested effort during studying-implying that motivational regulation can buffer against specific motivational problems occurring in the learning process.
Keywords: higher education; motivational regulation; quality of strategy use; self-regulated learning; standardized learning diary.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep timing is more important than sleep length or quality for medical school performance.Chronobiol Int. 2013 Jul;30(6):766-71. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2012.763132. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Chronobiol Int. 2013. PMID: 23750895
-
[Relationships between motivational regulation strategies, motivational factors, and learning behaviors outside the classroom].Shinrigaku Kenkyu. 2017 Apr;88(1):86-92. doi: 10.4992/jjpsy.88.16308. Shinrigaku Kenkyu. 2017. PMID: 29630315 Japanese.
-
Promoting an active form of learning out-of-class via answering online "study questions" leads to higher than expected exam scores in General Biology.PeerJ. 2015 Oct 8;3:e1322. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1322. eCollection 2015. PeerJ. 2015. PMID: 26500828 Free PMC article.
-
How Is Learning Motivation Shaped Under Different Contexts: An Ethnographic Study in the Changes of Adult Learner's Motivational Beliefs and Behaviors Within a Foreign Language Course.Front Psychol. 2018 Aug 30;9:1603. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01603. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30214423 Free PMC article.
-
Have motivation theories guided the development and reform of medical education curricula? A review of the literature.Acad Med. 2012 Jun;87(6):735-43. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318253cc0e. Acad Med. 2012. PMID: 22534597 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness of Inquiry and Practice During Project Design Courses at a Technology University.Front Psychol. 2022 May 18;13:859164. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.859164. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35664202 Free PMC article.
-
Few more hidden variables which would fortify person centred approach of self-regulated learning.Can Med Educ J. 2019 Nov 28;10(4):e111-e112. eCollection 2019 Nov. Can Med Educ J. 2019. PMID: 31807231 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Regulating self-organized collaborative learning: the importance of homogeneous problem perception, immediacy and intensity of strategy use.Int J Comput Support Collab Learn. 2020;15(2):149-177. doi: 10.1007/s11412-020-09323-5. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Int J Comput Support Collab Learn. 2020. PMID: 32837406 Free PMC article.
-
Problem perception and problem regulation during online collaborative learning: what is important for successful collaboration?Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1351723. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1351723. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39315039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boekaerts M. (1995). Self-regulated learning: bridging the gap between metacognitive and metamotivation theories. Educ. Psychol. 30 195–200. 10.1207/s15326985ep3004_4 - DOI
-
- Boekaerts M. (1997). Self-regulated learning: a new concept embraced by researchers, policy makers, educators, teachers, and students. Learn. Instruct. 7 161–186. 10.1016/S0959-4752(96)00015-1 - DOI
-
- Boekaerts M. (1999). Self-regulated learning: where we are today. Int. J. Educ. Res. 31 445–457. 10.1016/S0883-0355(99)00014-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources