Three Therapeutic Strategies: Cinacalcet, Paricalcitol or Both in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Treatment in Hemodialysed Patients During 1-Year Observational Study-A Comparison
- PMID: 30804890
- PMCID: PMC6371033
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00040
Three Therapeutic Strategies: Cinacalcet, Paricalcitol or Both in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Treatment in Hemodialysed Patients During 1-Year Observational Study-A Comparison
Abstract
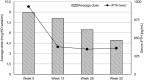
Introduction: Secondary hyperparathyroidism (sHPT) is a common hormonal complication of chronic kidney disease. There are several therapeutic options for sHPT management aiming at calcium-phosphorus balance normalization and decrease of parathormone secretion. Objectives: The aim of this retrospective, observational study was the outcome assessement of three most common therapeutic strategies of secondary hyperparathyroidism treatment with vitamin D receptor activator-paricalcitol, calcimimetic-cinacalcet or both agents administered together during in 12-months period. Methods: One hundred and thirty-one haemodialysed patients with uncontrolled parathyroid hormone secretion have been treated with paricalcitol administered intravenously (group PAR-60 patients) or cinacalcet per os (group CIN-50 patients). The last group (group PAR+CIN-21 patients) received paricalcitol i.v. and oral cinacalcet administered simultaneously. Results: In all groups, the iPTH level decreased significantly, however in group 1 treated with paricalcitol administered intravenously iPTH level decrease was greater than in group 2 treated with cinacalcet and in group 3 treated with paricalcitol and cinacalcet in parallel. The most substantial change of iPTH level was noticed after 3-months of observation. After this period the iPTH level was stabilized and maintained till the end of observation. Safety level of all strategies was comparable. No severe hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia was observed during the whole period of observation. Conclusions: The results of observation show significant advantage of intravenous paricalcitol treatment. Complementing cinacalcet therapy with paricalcitol does not improve treatment outcomes. In case of unsatisfactory results after 3-months treatment, potential continuation should be considered carefully. Among three available therapeutic options, the treatment with paricalcitol i.v. should be considered in all haemodialysed patients with inadequate control of serum PTH level. The second option-with cinacalced administered orally should be considered in PD patients and when severe hypercalcemia occurs.
Keywords: cinacalcet; hemodialysis; outcome; paricalcitol; secondary hyperparathyroidism; vitamin D.
Figures
References
-
- Paricalcitol Fresenius Summary of Product Characteristics Available online at: http://pub.rejestrymedyczne.csioz.gov.pl/ProduktSzczegoly.aspx?id=27016 (2018) (Accessed April 01, 2018).
-
- Mimpara Summary of Product Characteristics Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/2017/2017082813... (2018) (Accessed April 01, 2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources