New Insights for RANKL as a Proinflammatory Modulator in Modeled Inflammatory Arthritis
- PMID: 30804932
- PMCID: PMC6370657
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00097
New Insights for RANKL as a Proinflammatory Modulator in Modeled Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
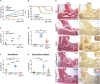
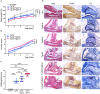
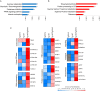
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL), a member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) superfamily, constitutes the master regulator of osteoclast formation and bone resorption, whereas its involvement in inflammatory diseases remains unclear. Here, we used the human TNF transgenic mouse model of erosive inflammatory arthritis to determine if the progression of inflammation is affected by either genetic inactivation or overexpression of RANKL in transgenic mouse models. TNF-mediated inflammatory arthritis was significantly attenuated in the absence of functional RANKL. Notably, TNF overexpression could not compensate for RANKL-mediated osteopetrosis, but promoted osteoclastogenesis between the pannus and bone interface, suggesting RANKL-independent mechanisms of osteoclastogenesis in inflamed joints. On the other hand, simultaneous overexpression of RANKL and TNF in double transgenic mice accelerated disease onset and led to severe arthritis characterized by significantly elevated clinical and histological scores as shown by aggressive pannus formation, extended bone resorption, and massive accumulation of inflammatory cells, mainly of myeloid origin. RANKL and TNF cooperated not only in local bone loss identified in the inflamed calcaneous bone, but also systemically in distal femurs as shown by microCT analysis. Proteomic analysis in inflamed ankles from double transgenic mice overexpressing human TNF and RANKL showed an abundance of proteins involved in osteoclastogenesis, pro-inflammatory processes, gene expression regulation, and cell proliferation, while proteins participating in basic metabolic processes were downregulated compared to TNF and RANKL single transgenic mice. Collectively, these results suggest that RANKL modulates modeled inflammatory arthritis not only as a mediator of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption but also as a disease modifier affecting inflammation and immune activation.
Keywords: RANKL; TNF; arthritis; inflammation; proteomics; transgenic models.
Figures




References
-
- Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1998) 95:3597–602. 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3597 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

