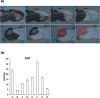
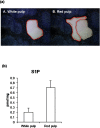
Measurement of the Spatial Distribution of S1P in Small Quantities of Tissues: Development and Application of a Highly Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method Combined with Laser Microdissection
- PMID: 30805275
- PMCID: PMC6372364
- DOI: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0072
Measurement of the Spatial Distribution of S1P in Small Quantities of Tissues: Development and Application of a Highly Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method Combined with Laser Microdissection
Abstract
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) acts as an extracellular signaling molecule with diverse biological functions. Tissues appear to have an S1P gradient, which is functionally relevant in the biological significance of S1P, although its existence has not been measured directly. Here, we report a highly sensitive method to determine the distribution of S1P, using a column-switching LC-MS/MS system combined with laser microdissection (LMD). Column switching using narrow core Capcell Pak C18 analytical and trap columns with 0.3 mm inner diameter improved the performance of the LC-MS/MS system. The calibration curve of S1P showed good linearity (r>0.999) over the range of 0.05-10 nM (1-200 fmol/injection). The accuracy of the method was confirmed by measuring S1P-spiked laser microdissected mice tissue sections. To evaluate our S1P analytical method, we quantified S1P extracted from micro-dissected mouse brain and spleen. These results show that this method can measure low S1P concentrations and determine S1P distribution in tissue microenvironments.
Keywords: column-switching LC-MS/MS; laser microdissection; sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Human Plasma Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Q-Tof Mass Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 18;18(8):1800. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081800. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28820460 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of sphingoid base-1-phosphates as bisacetylated derivatives by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Biochem. 2005 Apr 1;339(1):129-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2004.12.006. Anal Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15766719
-
Quantification of sphingosine 1-phosphate by validated LC-MS/MS method revealing strong correlation with apolipoprotein M in plasma but not in serum due to platelet activation during blood coagulation.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Nov;407(28):8533-42. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9008-4. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26377937 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of the method for the measurement of sphingosine-1-phosphate in biological samples and its application for S1P research].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Dec;118(6):383-8. doi: 10.1254/fpj.118.383. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11778456 Review. Japanese.
-
Immune regulation by sphingosine 1-phosphate and its receptors.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012 Feb;60(1):3-12. doi: 10.1007/s00005-011-0159-5. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2012. PMID: 22159476 Review.
Cited by
-
Density of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors Is Altered in Cortical Nerve-Terminals of Insulin-Resistant Goto-Kakizaki Rats and Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):338-347. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04033-4. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37794263 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophospholipid Mediators in Health and Disease.Annu Rev Pathol. 2022 Jan 24;17:459-483. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-050420-025929. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Annu Rev Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34813354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lymphatics in intestinal inflammation.Inflamm Regen. 2021 Aug 17;41(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41232-021-00175-6. Inflamm Regen. 2021. PMID: 34404493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Fix and Click" for Assay of Sphingolipid Signaling in Single Primary Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Anal Chem. 2022 Jan 25;94(3):1594-1600. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03503. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35020354 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced selective capture of phosphomonoester lipids enabling highly sensitive detection of sphingosine 1-phosphate.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Nov;415(26):6573-6582. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04937-8. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37736841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- S. R. Schwab, J. P. Pereira, M. Matloubian, Y. Xu, Y. Huang, J. G. Cyster. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science 309: 1735–1739, 2005. - PubMed