New diagnostic biomarker in acute diarrhea due to bacterial infection in children
- PMID: 30805506
- PMCID: PMC6372495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpam.2016.12.004
New diagnostic biomarker in acute diarrhea due to bacterial infection in children
Abstract
Background and objectives: Diarrhea is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children, and diarrhea may be due to infection that is bacterial or non-bacterial. Differentiation between diarrhea from a bacterial or non-bacterial infection is not a simple task, and no single method is present to differentiate between these causes of diarrhea.To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) and procalcitonin (PCT) in the diagnosis of acute diarrhea due to bacterial infection.
Patients and methods: Case control study of forty children with bacterial infection diarrhea diagnosed by stool culture and CRP, 40 children with acute non-bacterial infection diarrhea and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Stool cultures, serum CRP, PCT and serum sTREM-1 were measured in all children on admission.
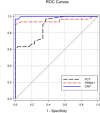
Results: Children with acute bacterial infection diarrhea had a significant increase in the serum sTREM-1 and PCT levels on admission compared to patients with nonbacterial infection diarrhea and controls (26.3667 ± 16.8184 ng/ml vs 7.2267 ± 6.4174 ng/ml vs 6.7367 ± 5.6479 ng/ml and 39.9933 ± 22.5260 ng/ml vs 1.8533 ± 1.7123 vs 0.2840 ± 0.1208 ng/ml, respectively; P < 0.05). sTREM-1 demonstrated significantly higher sensitivity (93.7%) and specificity (94.3%) in the prediction of bacterial infection as a cause of acute diarrhea in children with an area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve (95% CI) of 0.94 (0.84-0.99) at a cutoff value of 12.4 ng/ml.
Conclusions: Both serum PCT and sTREM-1 are valuable in the early diagnosis of acute bacterial infection-induced diarrhea in children, and there was markedly higher diagnostic discriminatory power for sTREM-1.
Keywords: Diarrhea; Procalcitonin (PCT); Soluble tregering expression on myeloid receptor type 1 (s TREM 1).
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Value of serum procalcitonin combined with soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in the differential diagnosis of bacterial and viral diarrhea in children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Aug;22(8):887-891. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2002191. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32800037 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Value of soluble TREM-1, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein serum levels as biomarkers for detecting bacteremia among sepsis patients with new fever in intensive care units: a prospective cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Jul 18;12:157. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-157. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22809118 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical and laboratory criteria for identification of early-onset stroke associated pneumonia: a prospective trial].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011 Jan;23(1):24-7. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2011. PMID: 21251362 Chinese.
-
Diagnostic value of the soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in lower respiratory tract infections: a meta-analysis.Respirology. 2014 May;19(4):501-7. doi: 10.1111/resp.12270. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Respirology. 2014. PMID: 24661408 Review.
-
PCT and sTREM-1: the markers of infection in critically ill patients?Med Sci Monit. 2008 Dec;14(12):RA241-7. Med Sci Monit. 2008. PMID: 19043381 Review.
Cited by
-
sTREM-1 as promising prognostic biomarker for acute-on-chronic liver failure and mortality in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 7;30(9):1177-1188. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1177. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38577193 Free PMC article.
-
Combating Childhood Infections in LMICs: evaluating the contribution of Big Data Big data, biomarkers and proteomics: informing childhood diarrhoeal disease management in Low- and Middle-Income Countries.EBioMedicine. 2021 Nov;73:103668. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103668. Epub 2021 Nov 3. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34742129 Free PMC article.
-
Pathobiome driven gut inflammation in Pakistani children with Environmental Enteric Dysfunction.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 23;14(8):e0221095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221095. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31442248 Free PMC article.
-
Serum/Faecal S100A12, CRP and lactoferrin can be used to distinguish ınfectious and non-ınfectious canine diarrhoea.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Nov;9(6):2485-2496. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1245. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37688789 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of non-invasive diagnostic tools for diarrhea: a systematic review of point-of-care tests and biomarkers.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Mar 15;86(5):2951-2962. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001946. eCollection 2024 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38694383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diarrhoeal disease Fact sheet N°330. World Health Organization; April 2013.
-
- Navaneethan U., Giannella R.A. Mechanisms of infectious diarrhea. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterology Hepatology. November 2008;5(11):637–647. - PubMed
-
- Diarrheal diseases in less developed countries. CDC; October 2013. Retrieved 28.
-
- Jamison D.T., Feachem R.G., Makgoba M.W., Bos Eduard R., Baingana Florence K., Hofman Karen J. 2nd ed. World Bank; Washington (DC): 2006. Disease and mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa. - PubMed
-
- Carbonnelle E. Laboratory diagnosis of bacterial meningitis: usefulness of various tests for the determination of the etiological agent. Médecine Maladies Infect. 2009;39:581–605. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous