Structure, dynamics and roX2-lncRNA binding of tandem double-stranded RNA binding domains dsRBD1,2 of Drosophila helicase Maleless
- PMID: 30805612
- PMCID: PMC6486548
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz125
Structure, dynamics and roX2-lncRNA binding of tandem double-stranded RNA binding domains dsRBD1,2 of Drosophila helicase Maleless
Abstract
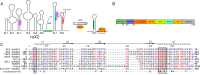
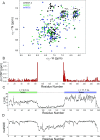
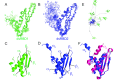
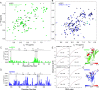
Maleless (MLE) is an evolutionary conserved member of the DExH family of helicases in Drosophila. Besides its function in RNA editing and presumably siRNA processing, MLE is best known for its role in remodelling non-coding roX RNA in the context of X chromosome dosage compensation in male flies. MLE and its human orthologue, DHX9 contain two tandem double-stranded RNA binding domains (dsRBDs) located at the N-terminal region. The two dsRBDs are essential for localization of MLE at the X-territory and it is presumed that this involves binding roX secondary structures. However, for dsRBD1 roX RNA binding has so far not been described. Here, we determined the solution NMR structure of dsRBD1 and dsRBD2 of MLE in tandem and investigated its role in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) binding. Our NMR and SAXS data show that both dsRBDs act as independent structural modules in solution and are canonical, non-sequence-specific dsRBDs featuring non-canonical KKxAXK RNA binding motifs. NMR titrations combined with filter binding experiments and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) document the contribution of dsRBD1 to dsRNA binding in vitro. Curiously, dsRBD1 mutants in which dsRNA binding in vitro is strongly compromised do not affect roX2 RNA binding and MLE localization in cells. These data suggest alternative functions for dsRBD1 in vivo.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Samata M., Akhtar A.. Dosage compensation of the X chromosome: a complex epigenetic assignment involving chromatin regulators and long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018; 87:323–350. - PubMed
-
- Migeon B.R. Choosing the active X: the human version of X inactivation. Trends Genet. 2017; 33:899–909. - PubMed
-
- Villa R., Schauer T., Smialowski P., Straub T., Becker P.B.. PionX sites mark the X chromosome for dosage compensation. Nature. 2016; 537:244–248. - PubMed
-
- Belote J.M., Lucchesi J.C.. Control of X chromosome transcription by the maleless gene in Drosophila. Nature. 1980; 285:573–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

